Metformin Treatment With or Without Mediterranean Diet for the Prevention of Age-Related Diseases in People With Metabolic Syndrome: The MeMeMe Randomized Trial
- PMID: 39641916
- PMCID: PMC11770154
- DOI: 10.2337/dc24-1597
Metformin Treatment With or Without Mediterranean Diet for the Prevention of Age-Related Diseases in People With Metabolic Syndrome: The MeMeMe Randomized Trial
Abstract
Objective: The Metformin and Dietary Restriction to Prevent Age-Related Morbid Events in People With Metabolic Syndrome (MeMeMe) trial tested whether 1,700 mg/day metformin (MET) with or without a Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) intervention could reduce the cumulative incidence of major noncommunicable diseases in people with metabolic syndrome.
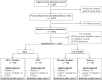
Research design and methods: A total of 1,442 participants were randomly assigned to one of four interventions: 1) MET (1,700 mg/day) plus MedDiet intervention (MET+MedDiet); 2) placebo plus MedDiet intervention; 3) MET (1,700 mg/day) alone; and 4) placebo alone. Participants were followed up for 3 years on average. The primary outcome was the cumulative incidence of major noncommunicable diseases (including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer). Secondary outcomes were the incidence of type 2 diabetes and the changing prevalence of metabolic syndrome.
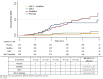
Results: The crude incidence of the major noncommunicable diseases was 6.7 cases per 100 person-years in the MET+MedDiet group, 6.9 in the MET alone group, 13.3 in the placebo plus MedDiet group, and 11.3 in the placebo group. The differences were fully explained by the reduction of type 2 diabetes, which was 80% and 92% lower in the MET and MET+MedDiet groups, respectively, compared with placebo.
Conclusions: The use of 1,700 mg/day MET is effective to prevent diabetes in people selected on the basis of metabolic syndrome.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, et al. .; International Association for the Study of Obesity . Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009;120:1640–1645 - PubMed
-
- Lakka H-M, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, et al. . The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 2002;288:2709–2716 - PubMed
-
- Hu G, Qiao Q, Tuomilehto J, Balkau B, Borch-Johnsen K, Pyorala K, DECODE Study Group . Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its relation to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in nondiabetic European men and women. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:1066–1076 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous