Interleukin-1 Blockade With RPH-104 (Goflikicept) in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Secondary End Points From an International, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2a Study
- PMID: 39642282
- PMCID: PMC11617079
- DOI: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001635
Interleukin-1 Blockade With RPH-104 (Goflikicept) in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Secondary End Points From an International, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2a Study
Abstract
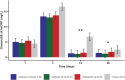
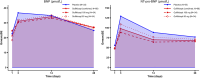
In a randomized double-blinded clinical trial of patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), goflikicept, an interleukin-1 blocker, significantly reduced systemic inflammation, measured as the area under the curve (AUC) for high-sensitivity C reactive protein at 14 days. We report secondary analyses of biomarkers at 28 days, and cardiac function and clinical end points at 1 year. Patients received a single administration of goflikicept 80 mg (n = 34), goflikicept 160 mg (n = 34), or placebo (n = 34). Both doses of goflikicept significantly reduced the AUC for high-sensitivity C reactive protein at 28 days compared with placebo, without statistically significant differences between the doses. There were no statistically significant differences between groups in the AUC for natriuretic peptides at 28 days. There were no significant differences between placebo, goflikicept 80 mg, and 160 mg groups in deaths (2.9%, 2.9%, and 0%), hospitalization for cardiovascular reasons (9.1%, 5.9%, and 0%), new-onset or progression of heart failure (9.1%, 5.9%, and 5.9%), and new or increased use of loop diuretics (24.2%, 14.7%, and 17.6%), nor in the number of patients with treatment emergent adverse events, with no treatment-related serious adverse events in any group. In conclusion, in patients with STEMI, interleukin-1 blockade with goflikicept 80 mg or 160 mg was well tolerated and associated with significant reduction of systemic inflammation. Further adequately powered studies are warranted to determine whether the reduction in systemic inflammation with goflikicept translates into a clinical benefit in patients with STEMI.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Abbate: Implicit Biosciences and Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals (consulting); Benjamin Van Tassell: Implicit Bioscience LLC (consulting), R-Pharm, NovoNordisk, Novartis (research grant); V. Bogin: Cromos Pharma (owner); Roshanak Markley: no conflict; D. V. Pevsner: Boston Scientific (consulting, research grant, lectures fee), R-Pharm (research grant), Novartis (research grant, travel grant); P. C. Cremer: Sobi, Kiniksa and CardiolRx (consulting), Kiniksa and Novartis (research grant); I. A. Meray: no conflict; D. V. Privalov: R-Pharm, Covance (EMPACT—MI), CSL Behring LLC (AEGIS-II)—research grant; Angela Taylor: Medical Advisory Board and Consultant for Boston Scientific; S. A. Grishin: employee of R-Pharm; A. N. Egorova: employee of R-Pharm; E. G. Ponomar: employee of R-Pharm; Yan Lavrovsky: employee of R-Pharm Overseas, Inc; M. Yu. Samsonov: employee of R-Pharm.
Figures

References
-
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al. . 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2018;39:119–177. - PubMed
-
- Del Buono MG, Garmendia CM, Seropian IM, et al. . Heart failure after ST-elevation myocardial infarction: beyond left ventricular adverse remodeling. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023;48:101215. - PubMed
-
- Abbate A, Salloum FN, Vecile E, et al. . Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, inhibits apoptosis in experimental acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2008;117:2670–2683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

