Deep learning biomarker of chronometric and biological ischemic stroke lesion age from unenhanced CT
- PMID: 39643604
- PMCID: PMC11624201
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01325-z
Deep learning biomarker of chronometric and biological ischemic stroke lesion age from unenhanced CT
Abstract
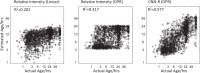
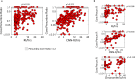
Estimating progression of acute ischemic brain lesions - or biological lesion age - holds huge practical importance for hyperacute stroke management. The current best method for determining lesion age from non-contrast computerised tomography (NCCT), measures Relative Intensity (RI), termed Net Water Uptake (NWU). We optimised lesion age estimation from NCCT using a convolutional neural network - radiomics (CNN-R) model trained upon chronometric lesion age (Onset Time to Scan: OTS), while validating against chronometric and biological lesion age in external datasets (N = 1945). Coefficients of determination (R2) for OTS prediction, using CNN-R, and RI models were 0.58 and 0.32 respectively; while CNN-R estimated OTS showed stronger associations with ischemic core:penumbra ratio, than RI and chronometric, OTS (ρ2 = 0.37, 0.19, 0.11); and with early lesion expansion (regression coefficients >2x for CNN-R versus others) (all comparisons: p < 0.05). Concluding, deep-learning analytics of NCCT lesions is approximately twice as accurate as NWU for estimating chronometric and biological lesion ages.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

