Mean pulmonary artery pressure prediction with explainable multi-view cardiovascular magnetic resonance cine series deep learning model
- PMID: 39645082
- PMCID: PMC11782807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jocmr.2024.101133
Mean pulmonary artery pressure prediction with explainable multi-view cardiovascular magnetic resonance cine series deep learning model
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a heterogeneous condition and regardless of etiology impacts negatively on survival. Diagnosis of PH is based on hemodynamic parameters measured invasively at right heart catheterization (RHC); however, a non-invasive alternative would be clinically valuable. Our aim was to estimate RHC parameters non-invasively from cardiac magnetic resonance (MR) data using deep learning models and to identify key contributing imaging features.
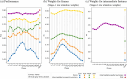
Methods: We constructed an explainable convolutional neural network (CNN) taking cardiac MR cine series from four different views as input to predict mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP). The model was trained and evaluated on 1646 examinations. The model's attention weight and predictive performance associated with each frame, view, or phase were used to judge its importance. Additionally, the importance of each cardiac chamber was inferred by perturbing part of the input pixels.
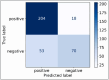
Results: The model achieved a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.80 and R2 of 0.64 in predicting mPAP and identified the right ventricle region on short-axis view to be especially informative.
Conclusion: Hemodynamic parameters can be estimated non-invasively with a CNN, using MR cine series from four views, revealing key contributing features at the same time.
Keywords: Deep learning; Explainable AI; Mean pulmonary artery pressure; Multi-view cardiac MR; Pulmonary hypertension.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interests The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Humbert M., Kovacs G., Hoeper M.M., Badagliacca R., Berger R.M.F., Brida M., et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertensionDeveloped by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Eur Heart J. 2022;43(38):3618–3731. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper M.M., Lee S.H., Voswinckel R., Palazzini M., Jais X., Marinelli A., et al. Complications of right heart catheterization procedures in patients with pulmonary hypertension in experienced centers. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(12):2546–2552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

