CircPTPN11 inhibits the replication of Coxsackievirus B5 through regulating the IFN-I pathway by targeting miR-152-3p/SIRPA axis
- PMID: 39647532
- PMCID: PMC11699211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199508
CircPTPN11 inhibits the replication of Coxsackievirus B5 through regulating the IFN-I pathway by targeting miR-152-3p/SIRPA axis
Abstract
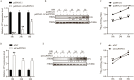
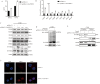
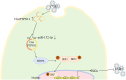
Coxsackievirus B5 (CVB5) is a major pathogen responsible for hand-foot-mouth disease, herpangina, and even severe death. The mechanisms underlying CVB5-induced diseases are not fully elucidated, and no specific antiviral treatments are currently available. Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a closed-loop molecular structure, have been reported to be involved in virus infectious diseases. However, their roles and mechanisms in CVB5 infection remain largely unknown. In this study, we identify that CircPTPN11 is significantly upregulated following CVB5 infection in RD cells. Characteristic analysis reveals that the expression of CircPTPN11 is both time- and dose-dependent upon CVB5 infection and is specific to intestinal tissue. Moreover, CircPTPN11 inhibits CVB5 replication by activating IRF3 in the type-I interferon (IFN-I) pathway. Further underneath mechanism shows that CircPTPN11 indirectly regulates CVB5 replication by sponging miR-152-3p, and miR-152-3p influences CVB5 replication by interacting with the gene coding for signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPA). In conclusion, this study suggests that CircPTPN11 targets SIRPA by sponging miR-152-3p, thereby inhibiting the replication and proliferation of CVB5. These findings provide a molecular target for the diagnosis and treatment of CVB5 infection.
Keywords: Circular RNAs (circRNAs); Coxsackieviruses group B5 (CVB5); Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD); IFN-I pathway; circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Alhazmi A., Nekoua M.P., Mercier A., Vergez I., Sane F., Alidjinou E.K., Hober D. Combating coxsackievirus B infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2023;33(1):e2406. - PubMed
-
- Chen L.L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):475–490. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Wang J., Wang C., Liu M., Zou Q. Deep learning models for disease-associated circRNA prediction: a review. Brief. Bioinform. 2022;23(6) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

