Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01116 Promotes the Proliferation of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting miR-9-5p/CCNE1 Axis
- PMID: 39648148
- PMCID: PMC11625508
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70270
Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01116 Promotes the Proliferation of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting miR-9-5p/CCNE1 Axis
Abstract
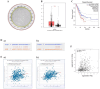
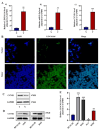
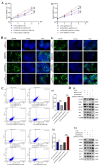
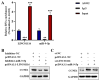
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) LINC01116 is crucial in promoting cell proliferation, invasion and migration in solid tumours, including lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). LINC01116 acts as a competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNA) that binds competitively to microRNAs and plays a critical role in tumour migration and invasion. However, other mechanisms of action besides the ceRNA theory have been rarely reported and remain to be elucidated further. The differences in RNA and protein levels in cells and tissues were assessed through real-time quantitative PCR and Western blot analysis. In vitro functional assays and in vivo xenograft models were used to analyse the function of LINC01116 in LUAD. Thus, the molecular correlation between miR-9-5p and CCNE1 was investigated through direct and indirect mechanism experiments. LINC01116, miR-9-5p and CCNE1 were upregulated in LUAD cell lines and tissues and were associated with a poor prognosis in patients. LINC01116 depletion inhibited proliferation but facilitated cell apoptosis. AGO2-RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation (AGO2-RIP) experiments confirmed that AGO2 binds to LINC01116 and miR-9-5p, indicating that LINC01116 interacts with miR-9-5p. The overexpression of miR-9-5p and CCNE1 effectively counteracts the biological effects of LINC01116 knockdown on reduced proliferation and cell cycle arrest in LUAD cells. The downregulation of miR-9-5p significantly reduces the CCNE1 level in A549 cells, and the upregulation of LINC01116 counteracts the downregulation of miR-9-5p effect, restoring the expression level of CCNE1. Our data demonstrated that LINC01116 regulates the expression of CCNE1 by positively regulating miR-9-5p, thereby affecting cell cycle, proliferation and participating in the development of LUAD.
Keywords: CCNE1; LINC01116; LUAD; cell proliferation; miR‐9‐5p.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Goldstraw P., Chansky K., Crowley J., et al., “The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer,” Journal of Thoracic Oncology 11, no. 1 (2016): 39–51, 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

