Contents of photosynthetic pigments and ratios of chlorophyll a/ b and chlorophylls to carotenoids (a+ b)/(x+ c) in C4 plants as compared to C3 plants
- PMID: 39648996
- PMCID: PMC11559476
- DOI: 10.32615/ps.2021.041
Contents of photosynthetic pigments and ratios of chlorophyll a/ b and chlorophylls to carotenoids (a+ b)/(x+ c) in C4 plants as compared to C3 plants
Abstract
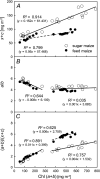
The content of chlorophylls (Chl) (a+b), total carotenoids (x+c), and the pigment ratios of Chl a/b and Chls to carotenoids (a+b)/(x+c) of green leaves of five C4 plants were determined and compared to those of C3 plants. The C4 plants were: Pacific and Chinese silvergrass (Miscanthus floridulus and Miscanthus sinensis), sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum) as well as feed and sugar maize (Zea mays). The three C3 plants were beech, ginkgo, and oak. C4 plants possess higher values for the ratio Chl a/b (3.4-4.5) as compared to the C3 plants (2.6-3.3). Sugar maize had the highest values for Chl a/b (4.04-4.70) and exceptionally high contents of total carotenoids and consequently lower values for the ratio of (a+b)/(x+c) (mean: 3.75 ± 0.6). During autumnal senescence also C4 plants showed a faster decline of Chl b as compared to Chl a yielding high values for Chl a/b of 6 to 8. Chlorophylls declined faster than carotenoids yielding low (a+b)/(x+c) values below 1.0.
Keywords: C3 plants; C4 plants; autumnal leaf senescence; chlorophyll contents; photosynthetic pigments; shade leaves; sun leaves; total carotenoid content.
Copyright: © 2022 Lichtenthaler and Babani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson J.M., Chow W.S., Park Y.-I.: The grand design of photosynthesis: Acclimation of the photosynthetic apparatus to environmental cues. – Photosynth. Res. 46: 129-139, 1995. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00020423 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Björkman O.: Responses to different quantum flux densities. – In: Lange O.L., Nobel P.S., Osmond C.B., Ziegler H. (ed.): Physiological Plant Ecology I. Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology. Vol. 12A. Pp. 57-107. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg: 1981. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-642-68090-8_4
-
- Boardman N.K.: Comparative photosynthesis of sun and shade plants. – Ann. Rev. Plant Physio. 28: 355-377, 1977. https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev.pp.28.060177.002035 - DOI
-
- Evert R.F., Russin W.A., Bosabalidis A.M.: Anatomical and ultrastructural changes associated with sink-to-source transition in developing maize leaves. – Int. J. Plant Sci. 157: 247-261, 1996. https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/10.1086/297344 - DOI
-
- Hatch M.D.: C4-photosynthesis: A historical overview. – In: Sage R.F., Monson R.K. (ed.): C4 Plant Biology. Pp. 17-46. Academic Press, San Diego: 1999. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780126144406500033?v...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
