Holliday junction recognition protein (HJURP) could reflect the clinical outcomes of lung adenocarcinoma patients, and impact the choice of precision therapy
- PMID: 39649097
- PMCID: PMC11621083
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1475511
Holliday junction recognition protein (HJURP) could reflect the clinical outcomes of lung adenocarcinoma patients, and impact the choice of precision therapy
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most prevalent subtype of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), characterized by poor prognosis and a high mortality rate. Identifying reliable prognostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
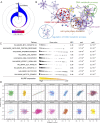
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive analysis of HJURP expression in LUAD using data from four cohorts: TCGA-LUAD (n = 453), GSE31210 (n = 226), GSE68465 (n = 442), and GSE72094 (n = 386). Univariate Cox regression analysis was employed to identify prognostic genes, with Kaplan-Meier survival analysis used to assess the predictive power of HJURP. Functional enrichment analyses were performed using MetaScape and FGSEA, and spatial transcriptomics and single-cell sequencing data were analyzed to explore HJURP's distribution and potential functions. Additionally, correlations between HJURP expression and genetic alterations, immune cell infiltration, and potential therapeutic responses were evaluated.
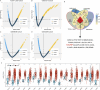
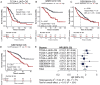
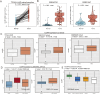
Results: HJURP was identified as a significant prognostic biomarker in all four cohorts, with high expression associated with increased risk of overall survival (OS) death (TCGA-LUAD: HR = 1.93, 95% CI: 1.321-2.815, P < 0.001; GSE31210: HR = 2.75, 95% CI: 1.319-5.735, P = 0.007; GSE68465: HR = 1.57, 95% CI: 1.215-2.038, P < 0.001; GSE72094: HR = 2.2, 95% CI: 1.485-3.27, P < 0.001). Functional analyses indicated that HJURP is involved in DNA metabolic processes, cell cycle regulation, and mitotic processes, with significant activation of pathways related to MYC targets, G2M checkpoint, and DNA repair. High HJURP expression was associated with higher mutation frequencies in TP53, CSMD3, TTN, and MUC16, and positively correlated with pro-inflammatory immune cell infiltration and several immune checkpoints, including PD-L1 and PD-L2. Chemotherapeutic agents such as gefitinib and sorafenib were predicted to be effective against high HJURP-expressing tumors.
Conclusion: HJURP is a pivotal biomarker for LUAD, consistently associated with poor prognosis and advanced disease stages. Its high expression correlates with specific genetic alterations and immune profiles, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. Future studies should validate these findings in larger cohorts.
Keywords: HJURP; genetic alterations; immune infiltration; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Zhang, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

