Improved cholera control in Kenya: A retrospective analysis of 2017-2019 in Nairobi and Homabay
- PMID: 39649439
- PMCID: PMC11622605
- DOI: 10.4102/jphia.v15i1.741
Improved cholera control in Kenya: A retrospective analysis of 2017-2019 in Nairobi and Homabay
Abstract
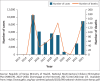
Background: Kenya has recorded at least 38 678 cases and 695 deaths over the last decade, and costing on average $2.2 million annually. From 2014 to 2016, the country experienced one of the deadliest and largest outbreak. However, between 2017 and 2020, there was a decline in the number of reported cases and deaths.
Aim: This study seeks to reveal the investments made post the 2014-2016 outbreak and highlight existing gaps that need to be addressed to stop the resurgence of cholera outbreaks in Kenya.
Setting: The study was conducted in two counties: Homabay and Nairobi.
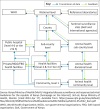
Methods: We used an observational study. Data were collected from 20 health facilities (involved in cholera control, during the study), 9 key informant interviews (KII) and 6 focus group discussions (FGDs).
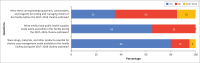
Results: We found improvement such as: dissemination of standard operating procedures, aligned reporting system, field epidemiology programme, establishment of a public health emergency operating centre and improved partner coordination. On the other hand, 12 of the selected 20 (60%) facilities had no prior training before government financing and laboratory capacity was sub-optimal: 13 (65%) facilities had no prior training, 16 (20%) had no operational laboratory plan and 10 (50%) had inadequate laboratory test kits and reagents.
Conclusion: This study highlights that Kenya has experienced an improvement in specific core capacities.
Contribution: For Kenya to completely flatten the curve, there is need for more sustainable investment and government's commitment in health system strengthening.
Keywords: Kenya; cholera; evaluation; response; surveillance.
© 2024. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships that may have inappropriately influenced them in writing this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systems, supplies, and staff: a mixed-methods study of health care workers' experiences and health facility preparedness during a large national cholera outbreak, Kenya 2015.BMC Public Health. 2018 Jun 11;18(1):723. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5584-5. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29890963 Free PMC article.
-
National surveillance data on the epidemiology of cholera in Kenya, 1997-2010.J Infect Dis. 2013 Nov 1;208 Suppl 1:S55-61. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit201. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24101646
-
A protracted cholera outbreak among residents in an urban setting, Nairobi county, Kenya, 2015.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Jun 25;36:127. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.127.19786. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 32849982 Free PMC article.
-
Trends of major disease outbreaks in the African region, 2003-2007.East Afr J Public Health. 2010 Mar;7(1):20-9. doi: 10.4314/eajph.v7i1.64672. East Afr J Public Health. 2010. PMID: 21413568 Review.
-
Landscape analysis of the Kenyan policy on the treatment and prevention of diarrheal disease among under-5 children.BMJ Open. 2024 Aug 19;14(8):e081906. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081906. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39160109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Republic of Kenya Ministry of Health . National Multi-Sectoral Cholera Elimination Plan (NMCEP). 2022–2030. [homepage on the Internet]. 2017. [cited 2024 Apr 17]. Available from: https://www.gtfcc.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/national-cholera-plan-k...
-
- World Bank . Republic of Kenya. Kenya loses KES27 billion annually because of poor sanitation, Washington DC, World Bank; 2012.
-
- Kenya Ministry of Health . National Multi-sectoral Cholera Elimination Plan(NMCEP) [homepage on the Internet]. 2022. [cited 2024 May 8]. Available from: https://www.gtfcc.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/national-cholera-plan-k...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources