Total burden of cerebral small vessel disease predict subjective cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39649721
- PMCID: PMC11621090
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1476701
Total burden of cerebral small vessel disease predict subjective cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Introduction: This study investigates the correlation between the total burden of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (CSVD) and Subjective Cognitive Decline (SCD) in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD).
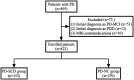
Methods: A cross-sectional design was employed, involving 422 patients with PD. Demographic and clinical data were collected. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was conducted to identify CSVD markers. SCD was assessed using the Cognitive Complaints Inventory (CCI).
Results: Logistic regression analyses revealed that the total burden of CSVD and specific imaging markers, including Deep White Matter Hyperintensities (DWMH), Periventricular Hyperintensities (PVH), and Enlarged Perivascular Spaces (EPVS), were significant predictors of SCD. The total burden of CSVD demonstrated the highest predictive accuracy for SCD in PD patients.
Discussion: The findings suggest that the total burden of CSVD, as measured by MRI, could serve as a potential biomarker for early identification of cognitive decline in PD, highlighting the importance of considering vascular factors in the early detection of cognitive changes in PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; cerebral small vessel disease; magnetic resonance imaging; predictive biomarkers; subjective cognitive decline.
Copyright © 2024 Qiu, Hu, Ge, Liu, Zhao, Lu, Tao and Xue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Blom K., Koek H. L., Zwartbol M. H. T., van der Graaf Y., Kesseler L., Biessels G. J., et al. . (2019). Subjective cognitive decline, brain imaging biomarkers, and cognitive functioning in patients with a history of vascular disease: the SMART-Medea study. Neurobiol. Aging 84, 33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.07.011, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cacciamani F., Houot M., Gagliardi G., Dubois B., Sikkes S., Sánchez-Benavides G., et al. . (2021). Awareness of cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13:697234. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.697234, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

