Correlation analysis of preoperative renal insufficiency with major complications in patients who received a radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: results of a retrospective observational analysis from a single center
- PMID: 39650069
- PMCID: PMC11621080
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1453346
Correlation analysis of preoperative renal insufficiency with major complications in patients who received a radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: results of a retrospective observational analysis from a single center
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to explore the factors affecting the major complications and the impacts of preoperative renal function on the incidence of complications in radical cystectomy procedures.
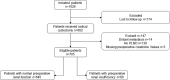
Methods: A retrospective review of 705 patients who received radical cystectomy between 2006 and 2021 was conducted. The 90-day complications of patients after a radical cystectomy were reported and the Clavien-Dindo classification (CDC) was used for grading complications. The clinical characteristics and preoperative outcomes were compared among patients with different preoperative renal functions. A logistic regression analysis of all patients was used to identify the risk factors associated with the major complications. Spearman's correlation analysis was used to examine the relationship between the classification of renal insufficiency and the CDC. In order to reduce the selection bias, one-to-one propensity score matching was performed, and the comparison of complications after matching was carried out for the sensitivity analysis.
Results: Within 90 days post-surgery, 71% of patients experienced complications, with 4.8% of them being major. Patients with preoperative renal insufficiency had a higher CDC and had a higher rate of major complications (16.7% vs 3.7%, p < 0.001). There was a linear relationship between preoperative serum creatinine and complications. Spearman's correlation analysis showed a slightly positive correlation between the classification of renal insufficiency and the CDC (r=0.094, p = 0.013). Preoperative renal insufficiency was a risk factor for major complications (OR = 6.805 [95%CI: 2.706-17.112]; p < 0.001). After matching, the patients in the preoperative renal insufficiency group had a higher CDC and a higher incidence of major complications (16.9% vs 1.7%, p = 0.004).
Conclusions: In our cohort, patients with preoperative renal insufficiency exhibited a higher incidence of complications following a radical cystectomy, and renal insufficiency was a significant risk factor for major complications.
Keywords: Clavien-Dindo; complications; radical cystectomy; renal function; renal insufficiency.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Huang, Hao and Xi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, Compérat E, Cowan NC, Efstathiou JA, et al. EAU guidelines on muscle invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. EAU Guidelines. (2021). doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.055 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources