The Impact of Cyberbullying Victimization on Internet Gaming Addiction Among College Students: The Mediating Roles of Basic Psychological Need Satisfaction and Frustration, and the Moderating Role of Parental Autonomy Support
- PMID: 39650088
- PMCID: PMC11624674
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S486250
The Impact of Cyberbullying Victimization on Internet Gaming Addiction Among College Students: The Mediating Roles of Basic Psychological Need Satisfaction and Frustration, and the Moderating Role of Parental Autonomy Support
Abstract
Purpose: Research on the relationship between cyberbullying victimization and Internet gaming addiction in China is limited, while the mechanisms underlying this association remain unclear. Based on the Self-Determination Theory, this study establishes a moderated mediation model to test the mediating roles of basic psychological need satisfaction and frustration between cyberbullying victimization and Internet gaming addiction, as well as the moderating role of parental autonomy support in this mediating effect.
Methods: 2819 college students were surveyed using self-reported questionnaires about cyberbullying victimization, basic psychological need satisfaction and frustration, parental autonomy support, and Internet gaming addiction. SPSS 24.0 was utilized to analyze the correlations between variables, and Amos 24.0 was employed to test the structural equation model of this study.
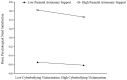
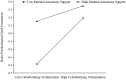
Results: Cyberbullying victimization was found to significantly predict Internet gaming addiction positively. Basic psychological need satisfaction and frustration played partial mediating roles between cyberbullying victimization and Internet gaming addiction respectively. Parental autonomy support further moderated the first half of the mediated model pathway. Specifically, the impact of cyberbullying victimization on basic psychological need satisfaction and frustration are more obvious among college students with high level of parental autonomy support.
Conclusion: The findings advance our understanding of how cyberbullying victimization affects Internet gaming addiction.Within the college environment, reducing cyberbullying victimization could prevent Internet gaming addiction. Furthermore, enhancing basic psychological need satisfaction, reducing basic psychological need frustration, and reinforcing parental autonomy support among college students who have experienced cyberbullying would be effective to prevent Internet gaming addiction.
Keywords: Cyberbullying victimization; basic psychological need; internet gaming addiction; parental autonomy support.
© 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Wang M, Qu X, Chen X, Wu X, Wang J. Harsh fathering longitudinally predicts adolescents’ internet gaming addiction via unfulfilled psychological need. Youth Soc. 2024;56(2):372–386. doi: 10.1177/0044118X231168 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

