Evaluation of Effect of Distraction Techniques Using Virtual Reality and Eight-dimension Audio Analgesia Methods on Pain Perception and Anxiety Levels in Children During Restorative Procedures: A Comparative In Vivo Study
- PMID: 39650306
- PMCID: PMC11617436
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2960
Evaluation of Effect of Distraction Techniques Using Virtual Reality and Eight-dimension Audio Analgesia Methods on Pain Perception and Anxiety Levels in Children During Restorative Procedures: A Comparative In Vivo Study
Abstract
Introduction: Dental pain and dental anxiety are the most common determinants of negative dental experience, the reason for broken appointments and ignored oral health care affecting the quality of life.
Aim: To evaluate the effects of distraction techniques using virtual reality and eight-dimension (8D) audio analgesia method on pain perception and anxiety levels in children during restorative procedures.
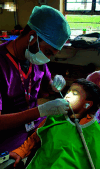
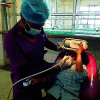
Materials and methods: A total of 120 children between the ages of 4 and 10 years old who visited for the first time to a pediatric dental department were grouped equally between three interventional groups. Group I was treated with conventional tell-show-do (TSD) method; patients selected for group II (8D audio analgesia) and group III (virtual reality method) underwent two-step procedure that initially involved the TSD technique, by explaining the distraction techniques method conditioned for restoration treatment. Clinical evaluation of anxiety levels was measured by using the Chotta Bheem-Chutki (CBC), face, legs, activity, cry, consolability (FLACC) scale, and recording pulse and oxygen saturation rate. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc Tukey's test was done to compare all the parameters between the three groups.
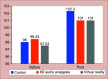
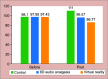
Results: In comparison to the conventional TSD method, both 8D audio analgesia and virtual reality method showed statistically better results. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's test showed no significant difference between the virtual reality group and 8D audio analgesic group.
Conclusion: Both 8D audio analgesia and virtual reality box distraction techniques can be used as an efficient distraction technique for TSD during dental procedures in children.
How to cite this article: Karuppiah M, Balamurugan SR, Rajashekaran S, et al. Evaluation of Effect of Distraction Techniques Using Virtual Reality and Eight-dimension Audio Analgesia Methods on Pain Perception and Anxiety Levels in Children During Restorative Procedures: A Comparative In Vivo Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2024;17(10):1087-1092.
Keywords: 8D audio analgesia; Anxiety; Behavior management techniques; Virtual reality.
Copyright © 2024; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: NoneConflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Virtual Reality Distraction, Audio Distraction and Tell-show-do Techniques in Reducing the Anxiety Level of Pediatric Dental Patients: An In Vivo Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021;14(Suppl 2):S173-S178. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2106. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021. PMID: 35645488 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Efficacy of Virtual Reality Distraction in Reducing Pain Perception and Anxiety in Children Aged 6-10 Years: A Behavioral Interventional Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019 Nov-Dec;12(6):510-513. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1694. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019. PMID: 32440065 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Eyeglasses as a Distraction Aid to Reduce Anxiety among 6-10-year-old Children Undergoing Dental Extraction Procedure.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019 Jul-Aug;12(4):297-302. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1640. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019. PMID: 31866714 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Audio and Audio-Visual Distraction Aids for Management of Pain and Anxiety in Children and Adults Undergoing Dental Treatment- A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 Mar 1;46(2):86-106. doi: 10.17796/1053-4625-46.2.2. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35533223
-
Virtual reality distraction for acute pain in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 22;10(10):CD010686. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010686.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33089901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attar RH, Baghdadi ZD. Comparative efficacy of active and passive distraction during restorative treatment in children using an iPad versus audiovisual eyeglasses: a randomised controlled trial. Eur Arch Paediat Dent. 2015;16:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Gardner WJ, Licklider JC. Auditory analgesia in dental operation. J Am Dental Assoc. 1959;59:1144–1150. - PubMed
-
- Roshan NM, Virupaxi SG, Bharath KP, et al. A comparative study of filmed modeling and tell-show-do technique on anxiety in children undergoing dental treatment. J Oral Health Comm Dent. 2018;12(1):20–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
