Clinical characteristics and biomarkers of severe immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis triggered by immunotherapy followed by radiation: a case report
- PMID: 39650655
- PMCID: PMC11621207
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454114
Clinical characteristics and biomarkers of severe immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis triggered by immunotherapy followed by radiation: a case report
Abstract
Background: The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has revolutionized the treatment landscape for tumor patients, dramatically improving survival rate. However, patients treated with immunotherapy are inevitably at risk of immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis (ICI-P) is an important type of IrAEs with a potentially lethal risk, which should be given more attention. Diagnosis and timely treatment of ICI-P is challenging due to the lack of specificity of its clinical and radiological features. Besides, poor understanding of biological mechanisms of ICI-P has led to a lack of reliable biomarkers to identify patients at risk, limiting timely treatment and proper management of it.
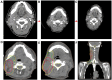
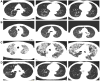
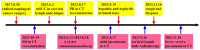
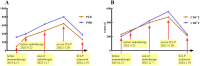
Case presentation: We presented longitudinal clinical features and successful treatment experience in a metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patient treated with immunochemotherapy followed by palliative radiotherapy for cervical lymph nodes who developed severe pneumonitis outside of the radiation field ten days after completion of radiotherapy suggestive of ICI-P. In addition, analysis of circulating biomarkers demonstrated an increase in platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and platelet-to-monocyte ratio (PMR), as well as the levels of CD4+T and CD8+T cells that tracked with the progression of ICI-P, and then decreased with corticosteroid treatment.
Conclusions: Our data highlight the imaging manifestations associated with ICI-related pulmonary toxicity and describe the dynamics of the corresponding circulating markers. Although our results reveal that dynamic monitoring of PLR and PMR as well as the levels of CD4+T and CD8+T cells may predict the risk of ICI-P, further investigations are needed to elucidate the underlying molecular and biological mechanisms for better management of ICI-P.
Keywords: biomarkers; immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis (ICI-P); immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); immune-related adverse event (irAE); immunotherapy; pneumonitis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Yu, Ren, Wu, Xu, Tian and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

