Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications - A Review
- PMID: 39651353
- PMCID: PMC11624689
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S487188
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications - A Review
Abstract
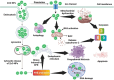
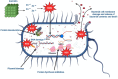
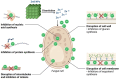
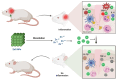
Over the last decade, biomedical nanomaterials have garnered significant attention due to their remarkable biological properties and diverse applications in biomedicine. Metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) are particularly notable for their wide range of medicinal uses, including antibacterial, anticancer, biosensing, cell imaging, and drug/gene delivery. Among these, zinc oxide (ZnO) NPs stand out for their versatility and effectiveness. Recently, ZnO NPs have become a primary material in various sectors, such as pharmaceutical, cosmetic, antimicrobials, construction, textile, and automotive industries. ZnO NPs can generate reactive oxygen species and induce cellular apoptosis, thus underpinning their potent anticancer and antibacterial properties. To meet the growing demand, numerous synthetic approaches have been developed to produce ZnO NPs. However, traditional manufacturing processes often involve significant economic and environmental costs, prompting a search for more sustainable alternatives. Intriguingly, biological synthesis methods utilizing plants, plant extracts, or microorganisms have emerged as ideal for producing ZnO NPs. These green production techniques offer numerous medicinal, economic, environmental, and health benefits. This review highlights the latest advancements in the green synthesis of ZnO NPs and their biomedical applications, showcasing their potential to revolutionize the field with eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions.
Keywords: antimicrobial; antioxidant; green synthesis; nanomedicine; nanoparticle; zinc oxide.
© 2024 El-Saadony et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Xie J, Cao Y, Jia D, Li Y, Wang Y. Solid-state synthesis of Y-doped ZnO nanoparticles with selective-detection gas-sensing performance. Ceram Int. 2016;42(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.07.135 - DOI
-
- Sun Y, Zhang W, Li Q, Liu H, Wang X. Preparations and applications of zinc oxide based photocatalytic materials. Adv Sens Energy Mater. 2023;2(3):100069. doi: 10.1016/j.asems.2023.100069 - DOI
-
- Adimule V, Revaigh MG, Adarsha HJ. Synthesis and fabrication of Y-doped ZnO nanoparticles and their application as a gas sensor for the detection of ammonia. J Mater Eng Perform. 2020;29:4586–4596. doi: 10.1007/s11665-020-04979-4 - DOI
-
- Izu N, Shimada K, Akamatsu T, Itoh T, Shin W, Shiraishi K, Usui T. Polyol synthesis of Al-doped ZnO spherical nanoparticles and their UV–vis–NIR absorption properties. Ceram Int. 2014;40(6):8775–8781. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.099 - DOI
-
- Mishra PN, Mishra PK, Pathak D. The influence of Al doping on the optical characteristics of ZnO nanopowders obtained by the low-cost sol-gel method. Chemistry. 2022;4(4):1136–1146. doi: 10.3390/chemistry4040077 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources