Peak systolic blood pressure during preparticipation exercise testing in 12,083 athletes: age, sex, and workload-indexed values and predictors
- PMID: 39651432
- PMCID: PMC11621218
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1456331
Peak systolic blood pressure during preparticipation exercise testing in 12,083 athletes: age, sex, and workload-indexed values and predictors
Abstract
Aim: Assessment of blood pressure during exercise is routine in athletes, but normal values remain equivocal. This study examines the response of systolic blood pressure (SBP) to exercise in a large cohort of athletes and establishes normative values by sex and age.
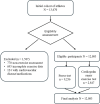
Methods: Competitive athletes free of cardiovascular disease underwent pre-participation exercise testing on a bicycle ergometer. Resting (SBPrest) and peak blood pressure (SBPpeak), heart rate (HRrest and HRpeak), and power output (WR) were recorded. Workload indexed values were calculated.
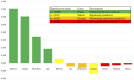
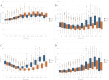
Results: The cohort included 12,083 athletes (median age 15 years, 26.9% female). Median peak exercise SBP was similar between sexes, but WR-indexed measures including SBP/WR ratio and SBP/(WR/kg) slope were higher in females (0.9 vs. 0.7, p < 0.001; 10.94 vs. 9.52, p < 0.001). Univariate analyses revealed significant associations between SBPpeak and several predictors, including sex, age, weight, height, SBPrest, DBPrest, HRrest, HRpeak, and WR (all p < .001). Multivariate analysis showed that SBPrest (beta = 0.353, 95% CI [0.541, 0.609], p < 0.001), height (beta = 0.303, 95% CI [0.360, 0.447], p < 0.001), WR (beta = 0.171, 95% CI [0.029, 0.045], p < 0.001), and age (beta = 0.093, 95% CI [0.162, 0.241], p < 0.001) were the strongest predictors of SBPpeak.
Conclusion: This study provides reference values for the interpretation of SBP responses to exercise in athletes. Multivariate analyses highlight the complex interplay of factors influencing peak SBP, including SBPrest, height, WR, age, DBPrest, sex, endurance sport category, and weight. In future studies, these findings may inform the development of personalised training strategies and risk stratification models in athletic populations.
Keywords: SBP/WR ratio; SBP/WR slope; athletes; blood pressure; exercise testing.
Copyright © 2024 Pesova, Jiravska Godula, Jiravsky, Jelinek, Sovova, Moravcova, Ozana, Ranic, Neuwirth, Miklik, Pekar, Sknouril, Tuka and Sovova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bauer P., Kraushaar L., Dörr O., Nef H., Hamm C. W., Most A. (2021). Sex differences in workload-indexed blood pressure response and vascular function among professional athletes and their utility for clinical exercise testing. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. červenec 121 (7), 1859–1869. 10.1007/s00421-021-04656-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biffi A., Gallo G., Fernando F., Sirico F., Signorello M. G., De Martino L., et al. (2022). Relationship between cardiorespiratory fitness, baseline blood pressure and hypertensive response to exercise in the ferrari corporate population. High. Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Hypertens. leden 29 (1), 81–88. 10.1007/s40292-021-00491-5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

