Decoding Dystonia in Autoimmune Disorders: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 39651491
- PMCID: PMC11623079
- DOI: 10.5334/tohm.915
Decoding Dystonia in Autoimmune Disorders: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: Dystonia is a common hyperkinetic movement disorder observed in various genetic, infective, drug-induced, and autoimmune disorders. Autoimmune disorders can present with isolated or combined acute or subacute dystonia. The pattern and approach to dystonia in autoimmune disorders are poorly described and have never been established in a structured manner.
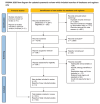
Objective: This scoping review aims to summarize all available clinical literature and formulate a pattern and approach to dystonia in different autoimmune disorders.
Methods: We included one hundred and three articles in this scoping review. Most articles identified were case reports or case series.
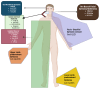
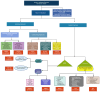
Results: In this review, we analysed data from 103 articles and summarized the epidemiological, clinical, and diagnostic features of dystonia associated with different autoimmune diseases. We highlight that dystonia can be isolated or combined in various autoimmune conditions and is responsive to immunotherapy. We point out the patterns of dystonia and associated neurological features and investigations that can suggest the underlying autoimmune nature, which can guide the most appropriate treatment.
Discussion: The clinical pattern of dystonia can be a unique feature in many autoimmune disorders. In isolated subacute dystonia, the presence of autoantibodies could have a temporal association, or this is just an epiphenomenon to be evaluated in further research.
Highlights: Many autoimmune disorders can present with isolated or combined dystonia.Subacute onset focal or segmental dystonia (craniocervical dystonia or limb dystonia) or hemidystonia could be secondary to an autoimmune condition and warrants investigations.They have a relapsing or progressive course.They usually have a good response to early immunotherapy.Symptomatic treatment, including botulinum toxin, can be useful in focal dystonia.
Keywords: autoimmune dystonia; autoimmune encephalitis; dystonia.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Jinnah HA, Hess, EJ. Evolving Concepts in the Pathogenesis of Dystonia. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5696051/. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol Theory Pract. 2005; 8(1): 19–32. DOI: 10.1080/1364557032000119616 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

