Teprotumumab versus intravenous methylprednisolone in thyroid eye disease: A systematic review
- PMID: 39651498
- PMCID: PMC11620316
- DOI: 10.4103/ojo.ojo_308_23
Teprotumumab versus intravenous methylprednisolone in thyroid eye disease: A systematic review
Abstract
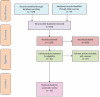
Thyroid eye disease (TED), also known as thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, is an autoimmune disorder caused due to a complex interplay between autoantigens including the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor and the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. TED is characterized by progressive proptosis or diplopia. This systematic review aimed to compare the efficacy of the newer monoclonal antibody - teprotumumab and intravenous methylprednisolone (IVMP) in TED patients. We performed a systematic review of previously published studies from 2013 to June 2023. A total of 329 articles were screened; among them, 111 non-duplicate publications were identified. After the screening of titles and abstracts, 156 publications were excluded; then, another 47 published papers were excluded after the full-text screening. The remaining 15 eligible studies were included in this systematic review. The majority of studies used either teprotumumab alone or in combination with others. Among 15 studies, eight studies used teprotumumab in TED patients, whereas remaining 7 studies used a standard treatment regimen. This systematic review provides an overview of the existing treatment options using monoclonal antibody - teprotumumab and IVMP in TED patients. The overall assessment provides a finding that antibody - teprotumumab is is a good choice compared to conventional IVMP for providing better outcomes in patients with TED.
Keywords: Antibody; graves ophthalmology; prednisone; teprotumumab; thyroid eye disease.
Copyright: © 2024 Oman Ophthalmic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bartalena L, Baldeschi L, Dickinson A, Eckstein A, Kendall-Taylor P, Marcocci C, et al. Consensus statement of the European Group on Graves’ orbitopathy (EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;158:273–85. - PubMed
-
- Bartalena L, Kahaly GJ, Baldeschi L, Dayan CM, Eckstein A, Marcocci C, et al. The 2021 European Group on Graves ‘Orbitopathy (EUGOGO) clinical practice guidelines for the medical management of Graves’ orbitopathy. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021;185:G43–67. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources