Plasma extracellular vesicle neurofilament light chain as the biomarkers of the progression of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39652080
- PMCID: PMC12010974
- DOI: 10.17305/bb.2024.11502
Plasma extracellular vesicle neurofilament light chain as the biomarkers of the progression of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
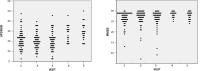
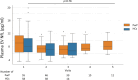
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive symptoms, underscoring the urgent need for predictive blood biomarkers. Plasma extracellular vesicles (EVs) offer a promising platform for biomarker development, with neurofilament light chain (NfL) emerging as a potential candidate for neurological diseases. This study evaluated plasma EV NfL as a biomarker for disease progression in a PD cohort.A total of 55 patients with PD (PwP) and 58 healthy controls (HCs) were followed, with PwP completing an average of 3.96 visits and HCs 2.25 visits. Plasma EVs were isolated and validated, and EV NfL levels were measured using an immunomagnetic reduction assay. Generalized estimating equations and Spearman correlations assessed relationships between clinical symptom progression and biomarkers. Although no significant differences in plasma EV NfL levels were observed between PwP and HCs over time, changes in plasma EV NfL significantly correlated with motor symptom progression, specifically with adjusted-total and akinetic-rigidity subscores of the Unified PD Rating Scale (UPDRS) Part III. Additionally, changes in UPDRS Part II scores were significantly associated with plasma EV NfL levels. These findings suggest that plasma EV NfL reflects motor symptom progression in PwP, highlighting its potential as a valuable biomarker for monitoring disease progression and guiding clinical trials in PD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma extracellular vesicle pathognomonic proteins as the biomarkers of the progression of Parkinson's disease.Biosci Trends. 2025 Mar 6;19(1):116-124. doi: 10.5582/bst.2024.01369. Epub 2025 Feb 9. Biosci Trends. 2025. PMID: 39924179
-
Neurofilament light chain level in plasma extracellular vesicles and Parkinson's disease.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2020 Dec 7;13:1756286420975917. doi: 10.1177/1756286420975917. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2020. PMID: 33335563 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Extracellular Vesicle α-Synuclein Level in Patients with Parkinson's Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 May 17;11(5):744. doi: 10.3390/biom11050744. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34067663 Free PMC article.
-
Blood neurofilament light chain in Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023 Jun;130(6):755-762. doi: 10.1007/s00702-023-02632-7. Epub 2023 Apr 17. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023. PMID: 37067597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood as a Biomarker for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(4):1353-1361. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190615. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31744001
References
-
- Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10291):2284–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00218-X. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong MJ, Okun MS. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA. 2020;323(6):548–60. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.22360. - PubMed
-
- Parnetti L, Gaetani L, Eusebi P, Paciotti S, Hansson O, El-Agnaf O, et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(6):573–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30024-9. - PubMed
-
- Fayyad M, Salim S, Majbour N, Erskine D, Stoops E, Mollenhauer B, et al. Parkinson’s disease biomarkers based on α-synuclein. J Neurochem. 2019;150(5):626–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14809. - PubMed
-
- Qu Y, Li J, Qin Q, Wang D, Zhao J, An K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of inflammatory biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis. 2023;9(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-023-00449-5. - PMC - PubMed

