Role of Dolutegravir/Lamivudine in the Management of Pregnant People Living with HIV-1: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39652285
- PMCID: PMC11782740
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-024-01085-z
Role of Dolutegravir/Lamivudine in the Management of Pregnant People Living with HIV-1: A Narrative Review
Abstract
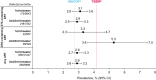
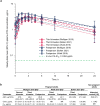
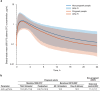
Lowering viral load during pregnancy is regarded as the most important method of reducing human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) vertical transmission risk, and minimizing fetal exposure to drugs is a guiding principle during pregnancy. Dolutegravir/lamivudine (DTG/3TC) has demonstrated high efficacy, a high barrier to resistance, and a good safety profile in non-pregnant individuals; however, DTG/3TC is not recommended by perinatal HIV treatment guidelines for initial therapy in pregnant people living with HIV-1 because of limited data on use of the 2-drug regimen during pregnancy. Efficacy and pharmacokinetic data from pregnant individuals using DTG and/or 3TC are reviewed and used to extrapolate anticipated DTG/3TC efficacy in pregnancy. There are robust data on the use of DTG- and 3TC-containing combination regimens, which are recommended by perinatal HIV treatment guidelines during pregnancy, supporting their well-established efficacy and safety in pregnant people living with HIV-1. Updated data from the Tsepamo and Eswatini surveillance studies (> 14,000 DTG exposures from conception) indicate no increased risk of neural tube defects with DTG. Pharmacokinetic data for DTG and 3TC indicate that exposures in pregnancy are within the therapeutically effective range seen in non-pregnant adults. Two studies evaluated DTG/3TC during pregnancy and both reported high virologic suppression rates [HIV-1 ribonucleic acid (RNA) < 50 copies/mL at delivery: 97% (30/31) overall], no events of vertical transmission, and no new safety signals, consistent with the use of DTG-based 3-drug regimens in pregnancy. The use of DTG/3TC during pregnancy is anticipated to be comparably effective and well tolerated for both parental health and prevention of vertical transmission with fetal exposure to fewer antiretrovirals compared with 3- or 4-drug regimens. These considerations are relevant when evaluating use of DTG/3TC in people living with HIV-1 who are pregnant or considering pregnancy in clinical practice and in perinatal HIV treatment guidelines.Video abstract available for this article. Supplementary file1 (MP4 319,147 KB).
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; Dolutegravir/lamivudine; HIV-1; Integrase strand transfer inhibitor; Pregnancy; Vertical transmission.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: William R. Short has received grants from Gilead Sciences (paid to institution), consulting fees from ViiV Healthcare, and honoraria from Janssen and ViiV Healthcare. Parul Patel, Ana Puga, Vani Vannappagari, Annemiek de Ruiter, and Bryn Jones are employees of ViiV Healthcare and own stock in GSK. Gustavo Verdier is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Ethical Approval: This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. The global health observatory: data on the HIV response. World Health Organization; 2024 [cited 2024 Jul 31]. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/hiv-aids/data-on-the-hiv-aids-r....
-
- UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS statistics—fact sheet. UNAIDS; 2024 [cited 2024 Jul 31]. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
-
- Wedi COO, Kirtley S, Hopewell S, Corrigan R, Kennedy SH, Hemelaar J. Perinatal outcomes associated with maternal HIV infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet HIV. 2016;3(1):e33–48. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

