Efficacy and safety of venetoclax plus azacitidine for patients with treatment-naive high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 39652823
- PMCID: PMC11923426
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2024025464
Efficacy and safety of venetoclax plus azacitidine for patients with treatment-naive high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
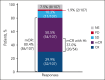
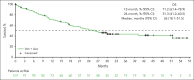
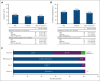
Outcomes are poor in patients with higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (HR MDS) and frontline treatment options are limited. This phase 1b study investigated safety and efficacy of venetoclax, a selective B-cell lymphoma 2 inhibitor, at the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D; 400 mg for 14 days per 28-day cycle), in combination with azacitidine (75 mg/m2 for 7 days per 28-day cycle) for treatment-naive HR MDS. Safety was the primary outcome, and complete remission (CR) rate was the primary efficacy outcome. Secondary outcomes included rates of modified overall response (mOR), hematologic improvement (HI), overall survival (OS), and time to next treatment (TTNT). As of May 2023, 107 patients received venetoclax and azacitidine combination at the RP2D. Best response of CR or marrow CR was observed in 29.9% and 50.5% (mOR, 80.4%), respectively. Median OS was 26.0 months, with 1- and 2-year survival estimates of 71.2% and 51.3%, respectively. Among 59 patients with baseline red blood cell and/or platelet transfusion-dependence, 24 (40.7%) achieved transfusion independence on study, including 11 (18.6%) in CR. Fifty-one (49.0%) of 104 evaluable patients achieved HI. Median TTNT excluding transplantation was 13.4 months. Adverse events reflected known safety profiles for venetoclax and azacitidine, including constipation (53.3%), nausea (49.5%), neutropenia (48.6%), thrombocytopenia (44.9%), febrile neutropenia (42.1%), and diarrhea (41.1%). Overall, venetoclax plus azacitidine at the RP2D was well tolerated and had favorable outcomes. A phase 3 study (NCT04401748) is ongoing to confirm survival benefit of this combination. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02942290.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.S.G. serves in an advisory role for AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, and Servier, and also received institutional funding from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Genentech, New Wave, Prelude, and Pfizer. U.P. serves as member of board of directors or advisory committee for Bristol Myers Squibb and MDS Foundation; and received honoraria, consultancy, and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Jazz, Syros, Servier, Silence Therapeutics, and Takeda; consultancy and research funding from Curis, Geron, and Janssen Biotech; research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, BeiGene, FibroGen, Roche, and Merk; reports consultancy with AbbVie; and reports honoraria from Celgene. O.O. served on the advisory board for Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, DSMB-Kymera Therapeutics, Novartis, Rigel, Servier, and Taiho; received research funding from AbbVie and AstraZeneca; and received institutional research support from Agios, Aprea, Astex, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, CTI, Daiichi Sankyo, Incyte, Janssen, Kartos, Novartis, NS-Pharma, and Oncotherapy Sciences. S.F. served on the board of directors or advisory committees for AbbVie, Astellas, Amgen, Ariad, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Pfizer; and received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer and Amgen and honoraria from AbbVie, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead/Kite and Amgen. C.Y.F. has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jazz, Novartis, Pfizer, and Servier; has acted as a consultant/adviser for AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jazz, Novartis, Pfizer, and Servier; and has received research funding from Amgen, Astellas, and Jazz. U.B. served on advisory board for Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Incyte, Rigel, Servier, Vincerx, Immunogen, and Sumitomo; received research support from AbbVie, Incyte, Jazz, and Novartis; and served on the independent data monitoring committee for Takeda. M.A.J. received honoraria from Gilead and research support from Jazz. D.N. received research funding from Affimed and Pharmaxis, and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb. M.R.B. received institutional research support from AbbVie; Ascentage; Astellas, Kite (a Gilead company), Kura, and Takeda. P.P. served on advisory board for Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Servier, and AbbVie; received honoraria from Jaxx and Astellas; and received research support from AbbVie, Jazz, and Astellas. G.K. is an employee with Genentech and may hold stock or other options in Roche. G.G.-M. received research support from AbbVie and Genentech. B.C., H.W., D.H., J.P. are employees with AbbVie and may hold stock or other options.
Figures


Comment in
-
Azacitidine and venetoclax for HR-MDS: election results pending.Blood. 2025 Mar 13;145(11):1099-1100. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024027567. Blood. 2025. PMID: 40080004 No abstract available.
References
-
- Garcia-Manero G, Chien KS, Montalban-Bravo G. Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2021 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(11):1399–1420. - PubMed
-
- Garcia JS, Swords RT, Roboz GJ, et al. A systematic review of higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes clinical trials to determine the benchmark of azacitidine and explore alternative endpoints for overall survival. Leuk Res. 2021;104 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

