Is There a Need for Functional Radiographs in Diagnosing Lumbar Instability?
- PMID: 39652825
- PMCID: PMC11629360
- DOI: 10.1177/21925682241306025
Is There a Need for Functional Radiographs in Diagnosing Lumbar Instability?
Abstract
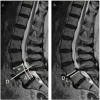
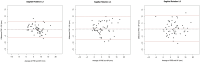
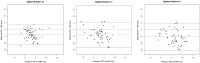
Study DesignRetrospective radiological database analysis.ObjectiveThe aim of this study was to assess the value of functional radiography (FRF = flexion; FRE = extension) compared to MRI and standing sagittal plane full spine radiography (SP) with low-grade spondylolisthesis.MethodsSagittal translation (ST) and rotation (SR) were measured between all lumbar levels to assess instability. The differences for ST and SR of SP and FRE as well as MRI and FRF were calculated. In addition, the lumbar lordosis, the sacral slope, the pelvic tilt and the pelvic incidence were measured.ResultsRadiological datasets of 55 patients with 165 lumbar segments fulfilled inclusion criteria. Instability was diagnosed in 20 segments (12.1%) with SP/MRI compared to 14 segments (8.5%) using FRF/FRE with ST. SR functional radiographs showed instability in 41 segments (25%) and 23 segments (14%) using SP/MRI. The intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) of ST between SP and FRE for L3/L4, L4/L5, and L5/S1 were 0.74, 0.84 and 0.97, respectively, indicating moderate to excellent agreement between imaging methods. For SP/FRE, the ICCs of the SR were 0.72, 0.61 and 0.64, respectively with moderate agreement. The ICCs of the ST for L3/4, L4/5, and L5/S1 showed moderate to good agreement between MRI and FRF with values of 0.52, 0.77, and 0.80, respectively. Regarding SR, poor agreement between MRI and FRF was observed. The ICCs for L3/4, L4/5, L5/S1 were 0.16, 0.23 and 0.23.ConclusionBased on our results, instability may also be diagnosed by calculating the difference in the ST in SP and MRI without additional functional radiographs. However, FRF showed translational instability more clearly than MRI in some patients and might still be an asset in borderline cases.
Keywords: functional radiography; lumbar spine; sagittal rotation; sagittal translation; segmental instability; spondylolisthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Dupuis PR, Yong-Hing K, Cassidy JD, Kirkaldy-Willis WH. Radiologic diagnosis of degenerative lumbar spinal instability. Spine. 1985;10(3):262-276. - PubMed
-
- Frymoyer JW, Selby DK. Segmental instability. Rationale for treatment. Spine. 1985;10(3):280-286. - PubMed
-
- Pope MH, Panjabi M. Biomechanical definitions of spinal instability. Spine. 1985;10(3):255-256. - PubMed
-
- Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Farfan HF. Instability of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982;165:110-123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

