A Case of Acute Contact Dermatitis Caused by Lidocaine/Prilocaine Cream on a Zoon Balanitis
- PMID: 39652940
- PMCID: PMC11620196
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.1404a281
A Case of Acute Contact Dermatitis Caused by Lidocaine/Prilocaine Cream on a Zoon Balanitis
Conflict of interest statement
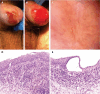
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
