Enhancing safety and quality in the global cheese industry: A review of innovative preservation techniques
- PMID: 39654744
- PMCID: PMC11625285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40459
Enhancing safety and quality in the global cheese industry: A review of innovative preservation techniques
Abstract
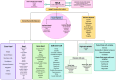
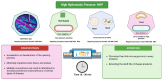
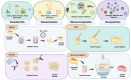
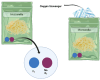
The global cheese industry faces challenges in adopting new preservation methods due to microbiological decay and health risks associated with chemical preservatives. Ensuring the safety and quality control of hard and semi-hard cheeses is crucial given their prolonged maturation and storage. Researchers are urged to create cheese products emphasizing safety, minimal processing, eco-labels, and clean labels to address consumer health and environmental worries. This review aims to explore effective strategies for ensuring the safety and quality of ripened cheeses, covering traditional techniques like aging, maturation, and salting, along with innovative methods such as modified and vacuum packaging, high-pressure processing, and active and intelligent packaging. Additionally, sustainable cheese preservation approaches, their impact on shelf life extension, and the physiochemical and quality attributes post-preservation are all analyzed. Overall, the cheese industry stands to benefit from this evaluation through enhanced market value, increased consumer satisfaction, and better environmental sustainability.The integration of novel preservation techniques in the cheese industry not only addresses current challenges but also paves the way for a more sustainable and consumer-oriented approach. By continually refining and implementing safety measures, quality control processes, and environmentally friendly practices, cheese producers can meet evolving consumer demands while ensuring the longevity and integrity of their products. Through a concerted effort to embrace innovation and adapt to changing market dynamics, the global cheese industry is poised to thrive in a competitive landscape where safety, quality, and sustainability are paramount.
Keywords: Active packaging; Cheese shelf-life; High-pressure processing; Modified atmosphere packaging.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- P.F. Fox, P.L. McSweeney, T.M. Cogan, T.P. Guinee, Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, Volume vol. 1: General aspects, Elsevier2004.
-
- Karoui R., Mouazen A.M., Dufour É., Pillonel L., Schaller E., De Baerdemaeker J., Bosset J.-O. Chemical characterisation of European Emmental cheeses by near infrared spectroscopy using chemometric tools. Int. Dairy J. 2006;16:1211–1217.
-
- Lucey J., Johnson M., Horne D. Invited review: perspectives on the basis of the rheology and texture properties of cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2003;86:2725–2743. - PubMed
-
- M. Østerlie, T. Wicklund, Food, nutrition, and health in Norway (including Svalbard), Nutritional and Health Aspects of Food in Nordic Countries, Elsevier2018, pp. 33-71.
-
- Skalkos D., Bamicha K., Kosma I.S., Samara E. Greek semi-hard and hard cheese consumers' perception in the new global era. Sustainability. 2023;15:5825.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

