Calcofluor White-Phosphatidylethanolamine Conjugate-Enhanced Ethosomal Delivery of Voriconazole for Targeting Candida albicans
- PMID: 39654804
- PMCID: PMC11626965
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S488456
Calcofluor White-Phosphatidylethanolamine Conjugate-Enhanced Ethosomal Delivery of Voriconazole for Targeting Candida albicans
Abstract
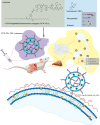
Introduction: The increasing prevalence of systemic fungal infections, especially among immunocompromised individuals, highlights the need for advancements in targeted and effective antifungal treatments. This study presents a novel nanomaterial, CFW-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (CFW-PEc), designed to enhance the delivery and efficacy of antifungal agents by targeting fungal cell walls through specific chitin binding. Ethosomes, lipid-based nanocarriers known for their ability to improve drug delivery across skin and cell membranes, were utilized in this study.
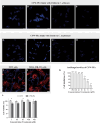
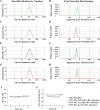
Methods: The physicochemical characteristics of voriconazole-loaded CFW-PEc ethosomes (CFW-PEc-VRC-ethosomes) were examined, including particle size, zeta potential, and entrapment efficiency. Antifungal efficacy of CFW-PEc-VRC-ethosomes was evaluated, including antifungal activity in vitro, CFW-PEc-ethosomes cellular uptake, and models of animal infection and imaging analyses.
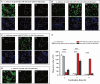
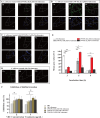
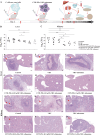
Results: In vitro experiments demonstrated a concentration-dependent inhibition of C. albicans growth by CFW-PEc, with cell inhibition rates reaching nearly 100% at 256 μM. In vivo investigations confirmed a 5-fold reduction in fungal burden in the liver and a 7.8-fold reduction in the kidney compared to the control group following treatment with CFW-PEc (0.1 μM)-VRC-ethosomes. Imaging analyses also confirmed the extended tissue retention of fluorescent dye-loaded CFW-PEc-ethosomes in mice, further underscoring their potential for clinical use.
Discussion: The targeted delivery of antifungal medications via ethosomes coated with CFW-PEc presents a promising strategy to improve antifungal effectiveness while reducing adverse effects, marking a significant advancement in fungal infection therapy.
Keywords: CFW-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate; antifungal agents; chitin binding; ethosomes; fungal cell walls.
© 2024 Shen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

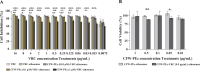

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

