Coexistent pleural effusion is found to be associated with aggravated subclinical myocardial injury in systemic lupus erythematous using cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 39654879
- PMCID: PMC11625759
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1504624
Coexistent pleural effusion is found to be associated with aggravated subclinical myocardial injury in systemic lupus erythematous using cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Objective: Pleural effusion (PE) is a common pulmonary manifestation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and is associated with disease activity. However, little is known regarding the additive effects of PE on cardiac function. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate multi-parameter cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) findings in SLE patients with PE and to explore whether cardiac involvement is associated with PE.
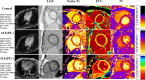
Methods: Patients with SLE and age-matched/sex-matched healthy controls were included in this study. Patients with SLE were diagnosed according to the 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria. Moreover, the PE diagnosis was based on computed tomography, and the height of the effusion was > 5 mm. All enrolled individuals underwent CMR imaging, including cine and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), T1, and T2 mapping imaging. The left and right ventricular function, LGE, T1, extracellular volume (ECV), and T2 values were evaluated.
Results: A total of 111 patients with SLE were enrolled, of whom 26 (23.42%) had PE. White cell count, hemoglobin, CRP, ESR, and lactate dehydrogenase levels were higher in SLE patients with PE than in SLE patients without PE (P<0.05). LGE was more prevalent in SLE patients with PE compared with those without PE (P<0.001). In addition, Native T1 (1348 ± 65 ms vs. 1284 ± 67 ms vs. 1261 ± 41 ms; P<0.001), ECV (31.92 ± 4.16% vs. 28.61 ± 3.60% vs. 26.54 ± 2.94%; P<0.001), and T2 (44.76 ± 3.68 ms vs. 41.96 ± 3.62 ms vs. 39.21 ± 2.85 ms; P<0.001) values were high in SLE patients with PE, intermediate in SLE patients without PE, and the lowest in the control group. Linear regression analysis demonstrated that PE was independently associated with LGE (β=0.329; P<0.05), T1 (β=0.346; P<0.05), ECV (β=0.353; P<0.05), and T2 (β=0.201; P<0.05).
Conclusions: SLE patients with PE have a higher prevalence of LGE and more diffuse myocardial fibrosis and edema than SLE patients without PE. Moreover, PE is associated with increased diffuse interstitial fibrosis and edema.
Keywords: T1 mapping; T2 mapping; cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging; late gadolinium enhancement; strains; systemic lupus erythematous.
Copyright © 2024 Zhi, Zhang, Zhu, Zou, You, Wen, Wang, Gao, Bing and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

