Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 39655055
- PMCID: PMC11627063
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2024-1080
Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma, a highly malignant skeletal tumor, primarily affects children and adolescents. Autophagy plays a crucial role in osteosarcoma pathophysiology. This study utilizes bibliometric analysis to evaluate current research on autophagy in osteosarcoma and forecast future directions.
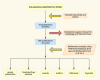
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of publications in the Web of Science Core Collection database from January 1, 2008, to March 15, 2024. Tools like VOSviewer, CiteSpace, R software, Excel, and Scimago were used for analysis and visualization.
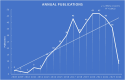
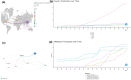
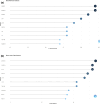
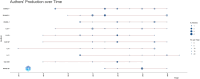
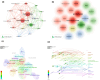
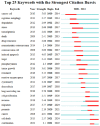
Results: Publications increased steadily over 17 years, indicating rising interest. Zhang Yuan was the most influential author, with Shanghai Jiao Tong University leading. Cell Death & Disease was the top journal. "HMGB1 Promotes Drug Resistance in Osteosarcoma" was the most cited paper. Co-cited articles focused on drug resistance, therapeutic targets, autophagy in cancer, and genomic impacts on immunotherapy. Keywords highlighted invasion, migration, cell death, and breast cancer as research hotspots. Future studies will likely focus on therapeutic innovations and integrated management strategies.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis offers an overview of current knowledge and emerging trends in autophagy and osteosarcoma, emphasizing key areas like invasion, migration, and cell death. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers developing novel therapies for osteosarcoma.
Keywords: autophagy; bibliometric analysis; cell death; invasion; osteosarcoma.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors affirm that the conduct of this research was not influenced by any commercial or financial affiliations that could be perceived as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Moosavi MA, Haghi A, Rahmati M, Taniguchi H, Mocan A, Echeverría J, et al. Phytochemicals as potent modulators of autophagy for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2018;424:46–69. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
