Salvage chemotherapy after progression on immunotherapy in recurrent/metastatic squamous cell head and neck carcinoma
- PMID: 39655068
- PMCID: PMC11625818
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1458479
Salvage chemotherapy after progression on immunotherapy in recurrent/metastatic squamous cell head and neck carcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: Anti-PD-(L)1 agents changed the landscape of recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (R/M HNSCC) treatment. Previous studies showed improved response rates to salvage chemotherapy (SCT) after progression to anti-PD-(L)1 agents. This study aims to evaluate the outcomes of SCT and to identify predictors of response and survival in patients with R/M HNSCC.
Materials and methods: Retrospective cohort analysis of 63 R/M patients treated with SCT after antiPD-(L1)-based therapy between January 2015 and August 2022. The overall response rate (ORR) was evaluated. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated with Kaplan-Meier method. Progression-free survival 2 was calculated from anti-PD-(L)1-therapy start until progression to SCT (PFS2-I). Logistic regression and Cox regression analyses were performed to identify predictors of outcome.
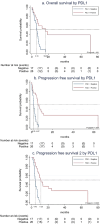
Results: A total of 63 patients were included: 76% were men, and median age was 60 years. PD-L1 status was available in 68% (61% positive). Up to 71% received SCT as third line or beyond. ORR to SCT was 49% with higher rates in PD-L1 positive tumors, 71% vs. 18% (p=0.001), and cetuximab-containing regimens, 68% vs. 39% (p=0.026). PD-L1 status was the only predictor of ORR in the adjusted model (OR=8.6, 95% CI 1.7-43.0). OS and PFS were 9.3 months (95% CI, 6.5-12.3) and 4.1 months (95% CI, 3.0-5.8) respectively. PFS2-I was 8.6 months (95% CI, 6.6-10.5). In the multivariate analysis, PD-L1 was the only independent factor for OS (HR=0.3; 95% CI, 0.1-0.7), PFS (HR=0.2; 95% CI, 0.1-0.5; p<0.001), and PFS2-I (HR=0.2; 95% CI 0.1-0.5; p<0.001).
Conclusion: PDL1 status appeared as a strong predictor of response of efficacy for SCT after anti-PD-(L)1 agents. Patients receiving cetuximab-containing regimens trended towards greater benefit. This highlights the importance of treatment sequencing and personalized treatment strategies.
Keywords: HNSCC; SCT; anti-PD-(L)1; head and neck; immunotherapy; salvage chemotherapy; squamous cell carcinoma; treatment sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Llop, Plana, Tous, Ferrando-Díez, Brenes, Juarez, Vidales, Vilajosana, Linares, Arribas, Duch, Fulla, Brunet, Lozano, Cirauqui, Mesía and Oliva.
Conflict of interest statement
SL has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: MSD, Merck. MP has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: Eisai and MSD. ST has sponsorship for grants from Merck, Roche, GSK, IDT, Hologic, Seegene. AF-D has speaker’s Bureau: MSD and Angelini Pharma; and travel accommodations expenses: MSD, Lilly, Roche, Merck, BMS, and Pfizer. JB has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: MSD, Merck. MJ has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: MSD, Merck. ZV has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: MSD, Merck. EV has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: MSD, Merck. IL has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: Merck. LA has advisory arrangements with Pfizer, Nutricia; Speaker’s Bureau: MSD, Merck, Nestle; Travel accommodations expenses: Nestle, Vegenat. AL has speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: Merck. BC has advisory arrangements: BMS, Merck and MSD; Training grants: BMS, Merck and MSD; Speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: BMS, Merck and MSD. RM has consulting/advisory arrangements with Pfizer, MSD, Merck KgA, Boehringer, GSK; Speakers’ Bureau: Merck KgA, MSD, Roche. MO has consulting/advisory arrangements with Merck, MSD and Transgene. Research support from Merck and Roche. The institution receives clinical trial support from Abbvie, Ayala Pharmaceutical, MSD, ALX Oncology, Debiopharm International, Merck, ISA Pharmaceuticals, Roche Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Seagen, Gilead. Speaker’s Bureau/Travel accommodations expenses: BMS, MSD, Merck. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. (2019) 394:1915–28. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Trufero J, Isla D, Adansa JC, Irigoyen A, Hitt R, Gil-Arnaiz I, et al. Phase II study of capecitabine as palliative treatment for patients with recurrent and metastatic squamous head and neck cancer after previous platinum-based treatment. Br J Cancer. (2010) 102:1687–91. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605697 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Machiels JP, René Leemans C, Golusinski W, Grau C, Licitra L, Gregoire V. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS–ESMO–ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1462–75. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.011 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials