Automated method of bronchus and artery dimension measurement in an adult bronchiectasis population
- PMID: 39655177
- PMCID: PMC11626611
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00231-2024
Automated method of bronchus and artery dimension measurement in an adult bronchiectasis population
Abstract
Aim: Bronchiectasis (BE) is a disease defined by irreversible dilatation of the airway. Computed tomography (CT) plays an important role in the detection and quantification of BE. The aim of this study was three-fold: 1) to assess bronchus-artery (BA) dimensions using fully automated software in a cohort of BE disease patients; 2) to compare BA dimensions with semi-quantitative BEST-CT (Bronchiectasis Scoring Technique for CT) scores for BE and bronchial wall thickening; and 3) to explore the structure-function relationship between BA-method lumen dimensions and spirometry outcomes.
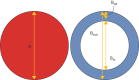
Methods: Baseline CTs of BE patients who participated in a clinical trial were collected retrospectively. CTs were analysed manually with the BEST-CT scoring system and automatically using LungQ (v.2.1.0.1, Thirona, The Netherlands), which measures the following BA dimensions: diameters of bronchial outer wall (Bout), bronchial inner wall (Bin) and artery (A), and bronchial wall thickness (Bwt) and computes BA ratios (Bout/A and Bin/A) to assess bronchial widening. To assess bronchial wall thickness, we used the Bwt/A ratio and the ratio between the bronchus wall area (Bwa) and the area defined by the outer airway (Boa) (Bwa/Boa).
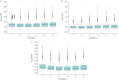
Results: In total, 65 patients and 16 900 BA pairs were analysed by the automated BA method. The median (range) percentage of BA pairs defined as widened was 69 (55-84)% per CT using a cut-off value of 1.5 for Bout/A, and 53 (42-65)% of bronchial wall were thickened using a cut-off value of 0.14 for Bwt/A. BA dimensions were correlated with comparable outcomes for the BEST-CT scoring method with a correlation coefficient varying between 0.21 to 0.51. The major CT BA determinants of airflow obstruction were bronchial wall thickness (p=0.001) and a narrower bronchial inner diameter (p=0.003).
Conclusion: The automated BA method, which is an accurate and sensitive tool, demonstrates a stronger correlation between visual and automated assessment and lung function when using a higher cut-off value to define bronchiectasis.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Author contributions: A.L.P. Pieters contributed to the design of the work, data collection and drafted the manuscript up to the final version. Q. Lv contributed to the data collection, analyses and gave final approval for the manuscript. J.J. Meerburg contributed to the data collection for her previous studies. E-R. Andrinopoulou contributed to the analyses and gave final approval for the manuscript. H.A.W.M. Tiddens contributed to the design and analyses of the work and gave final approval for the manuscript. T. van der Veer, P. Ciet, J.D. Chalmers, M.R. Loebinger, C.S. Haworth and J.S. Elborn contributed to the design of the work and gave final approval for the manuscript. Conflict of interest: A.L.P. Pieters, Q. Lv, T. van der Veer, J.J. Meerburg, J.S. Elborn and E-R. Andrinopoulou declare no conflict of interest. Conflict of interest: P. Ciet has received grants or contract fees from NOW-Dutch Research Council and Horizon Pathfinder; and has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations etc. from Chiesi and Vertex, and travel support from the European Respiratory Society. He holds a leadership role as Chair of the Thoracic Group of the Cardiothoracic Taskforce of the European Society of Pediatric Radiology. Conflict of interest: J.D. Chalmers has received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Grifols, Novartis, Insmed and Trudell; has received consultancy or speaker fees from Antabio, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Trudell and Zambon; and is an associate editor of this journal. Conflict of interest: M.R. Loebinger has received consulting fees from Armata, 30T, AstraZeneca, Parion, Ismed, Chiesi, Zambon, Electromed, Recode and Boehringer Ingelheim; and has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations etc. from Chiesi, Insmed, Mylan and Zambon. Conflict of interest: C.S. Haworth has received consulting fees from 30 Technology, CSL Behring, Chiesi, Ismed, Janssen, LifeArc, Meiji, Mylan, Pneumagen, Shionogi, Vertex and Zambon; and has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations etc. from Chiesi, Ismed, Mylan and Zambon. Conflict of interest: H.A.W.M. Tiddens is professor emeritus at Erasmus MC and the CMO of Thirona; he has received consulting fees for Insmed, Chiesi and Boehringer, a provides paid courses for Vertex.
Figures

References
-
- Bahous J, Cartier A, Pineau L, et al. . Pulmonary function tests and airway responsiveness to methacholine in chronic bronchiectasis of the adult. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 1984; 20: 375–380. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
