Improvement of contact lens-associated dry eye disease with the use of hydrogen peroxide
- PMID: 39655327
- PMCID: PMC11627073
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18482
Improvement of contact lens-associated dry eye disease with the use of hydrogen peroxide
Abstract
Background: The dropout rate of contact lens users has not decreased significantly over the years. Despite continuous improvements in contact lens (CL) designs, materials and surface treatments, the number of CL users who drop out remains similar to the number of new CL users. The aim of this study is to analyse the improvement in contact lens-associated dry eye disease (CLADE), quantified with the OSDI questionnaire when changing maintenance system solution from multipurpose solution to hydrogen peroxide.
Methods: This study included contact lens users for over a year as the multipurpose solution for the maintenance system, suffering from CLADE, and those who scored over 13 in the ocular surface disease index questionnaire, and did not manifest any clinical signs over 3 in the EFRON scale. The non-parametric data distribution was verified with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test, which was used to compare the visual acuity (VA), OSDI score and bulbar redness (EFRON scale) of the follow-up visit against the baseline value.
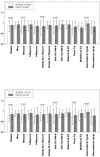
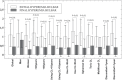
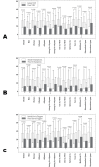
Results: Thirty-eight patients were included. Analysing the clinical parameters between the initial and final visit after one month of hydrogen peroxide use, a statistically significant improvement was found in the VA, bulbar hyperemia, OSDI scale and their subscales of the total sample (P < 0.04).
Conclusion: This study is intended as a first step towards a standardised protocol of actions to improve CLADE in an attempt to reduce contact lens dropout using OSDI as a tool for detection.
Keywords: CLADE; Contact lens; Contact lens dropout; Contact lens-associated dry eye disease; Dryness; EFRON scale; Hydrogen peroxide; Hyperemia; OSDI; Ocular discomfort.
©2024 Castro et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Susana Castro, Laura Garcia-Aguilar, Eduardo Garcia-Brion, Sofia Perez-Garcia, Consuelo Rosique and Carmelo Baños are employed by General Optica.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lid Papillae Improvement with Hydrogen Peroxide Lens Care Solution Use.Optom Vis Sci. 2016 Aug;93(8):933-42. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000890. Optom Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27232899 Clinical Trial.
-
Validation and repeatability assessment of the Chinese version of the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), 5-item dry eye (DEQ-5), and contact lens dry eye questionnaire-8 (CLDEQ-8) questionnaires.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2025 Jun;48(3):102353. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2024.102353. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2025. PMID: 39694733
-
Ocular thermography and clinical measurements in symptomatic and asymptomatic soft contact lens wearers.Optom Vis Sci. 2024 Sep 1;101(9):595-602. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000002177. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Optom Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39259709
-
Advances in Contact Lens Care Solutions: PVP-I Disinfectant and HAD Wetting Agents From Japan.Eye Contact Lens. 2024 Feb 1;50(2):91-101. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000001060. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Eye Contact Lens. 2024. PMID: 38019569 Review.
-
2. Contact lens care and ocular surface homeostasis.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2013 Jan 15;36 Suppl 1:S9-13. doi: 10.1016/S1367-0484(13)60004-1. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2013. PMID: 23347575 Review.
References
-
- Craig JP, Nelson JD, Azar DT, Belmonte C, Bron AJ, Chauhan SK, de Paiva C, Gomes JAP, Hammitt KM, Jones L, Nichols JJ, Nichols KK, Novack GD, Stapleton FJ, Wilcox MDP, Wolffsohn JS, Sullivan DA. TFOS DEWS II report executive summary. Ocular Surface. 2017;15:802–812. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2017.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Craig JP, Willcox MDP, Argüeso P, Maissa C, Stahl U, Tomlinson A, Wang J, Yokoi N, Stapleton F. The TFOS international workshop on contact lens discomfort: report of the contact lens interactions with the tear film subcommittee. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2013;54:123–156. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Queiruga J, Pena-Verdeal H, Ferreiro-Figueiras D, Noya-Padin V, Giraldez MJ, Yebra-Pimentel E. Assessing neophyte response to daily disposable silicone hydrogel contact lenses: a randomised clinical trial investigation over one month. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics. 2024;44:876–883. doi: 10.1111/opo.13328. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

