Characterization of Shigella flexneri serotype 6 strains from geographically diverse low- and middle-income countries
- PMID: 39655936
- PMCID: PMC11708030
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02210-24
Characterization of Shigella flexneri serotype 6 strains from geographically diverse low- and middle-income countries
Abstract
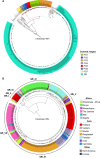
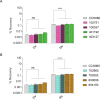
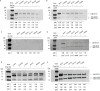
Shigella flexneri serotype 6 (Sf6) is one of the most common serotypes recovered from surveillance studies of moderate to severe diarrhea. Despite the clinical significance of Sf6, this serotype is understudied. In this work, we have performed both serotype-specific genomic and phenotypic comparisons of Sf6 isolates to one another and non-S. flexneri serotypes. Comparative genomic analyses identified significant nucleotide homology between Sf6 strains (n = 325), despite a broad range of collection timeframes and geographic locations. We identified Sf6 specific factors, including a potential novel Shigella virulence factor (type II secretion system). Additionally, we identified established Shigella virulence genes (ospG) and metabolic genes (rutABCDEFGR) that were absent in Sf6 strains while present in the majority of 728 non-Sf6 strains. Complete sequencing of 11 clinical Sf6 strains, demonstrated that the Sf6 virulence plasmid (pINV) is ~38 kb smaller than the average non-Sf6 pINV (~228 kb). Comparisons of S. flexneri species level antibiotic susceptibility highlighted that clinical Sf6 isolates from Africa in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS) and Vaccine Impact on Diarrhea in Africa (VIDA) study demonstrated geographic, serotype-specific susceptibility pattern. Phenotypic analyses of Sf6 identified reduced intracellular invasion and cytokine induction from HT-29 cells, as well as reduced Ipa protein effector secretion, compared with S. flexneri serotype 2a strain 2457T. Together these data highlight conserved and unique serotype-specific genotypic and phenotypic features for Sf6. This level of conservation has not been noted for other S. flexneri serotypes and is promising for vaccine and diagnostic assays to provide global Sf6-specific coverage.IMPORTANCEShigellosis is an ongoing global public health crisis with >270 million annual episodes among all age groups; however, the greatest disease burden is among children in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC). The lack of a licensed Shigella vaccine and the observed rise in antimicrobial-resistant Shigella spp. highlights the urgency for effective preventative and interventional strategies. The inclusion of S. flexneri serotype 6 (Sf6) is a necessary component of a multivalent vaccine strategies based on its clinical and epidemiological importance. Given the genomic diversity of Sf6 compared with other S. flexneri serotypes and Sf6 unique O-antigen core structure, serotype-specific characterization of Sf6 is a critical step to inform Shigella-directed vaccine and alternative therapeutic designs. Herein, we identified conserved genomic content among a large collection of temporally and geographically diverse Sf6 clinical isolates and characterized genotypic and phenotypic properties that separate Sf6 from non-Sf6 S. flexneri serotypes.
Keywords: Shigella; Shigella flexneri; Shigella flexneri serotype 6; comparative genomics; host-pathogen interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators . 2018. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392:1736–1788. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Platts-Mills JA, Juma J, Kabir F, Nkeze J, Okoi C, Operario DJ, Uddin J, Ahmed S, Alonso PL, et al. . 2016. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to identify causes of diarrhoea in children: a reanalysis of the GEMS case-control study. Lancet 388:1291–1301. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31529-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017 Diarrhoeal Disease Collaborators . 2020. Quantifying risks and interventions that have affected the burden of diarrhoea among children younger than 5 years: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect Dis 20:37–59. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30401-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Connor TR, Barker CR, Baker KS, Weill F-X, Talukder KA, Smith AM, Baker S, Gouali M, Pham Thanh D, Jahan Azmi I, Dias da Silveira W, Semmler T, Wieler LH, Jenkins C, Cravioto A, Faruque SM, Parkhill J, Wook Kim D, Keddy KH, Thomson NR. 2015. Species-wide whole genome sequencing reveals historical global spread and recent local persistence in Shigella flexneri. Elife 4:e07335. doi:10.7554/eLife.07335 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
