Early bactericidal activity of sitafloxacin against pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 39656013
- PMCID: PMC11705927
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01645-24
Early bactericidal activity of sitafloxacin against pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
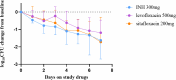
Sitafloxacin is a quinolone broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, and its pharmacologic properties and in vitro data demonstrate that sitafloxacin has a potent killing effect against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including drug-resistant strains, which is superior to that of other available quinolones. However, its efficacy in patients with primary-sensitive tuberculosis is unclear. This study aims to evaluate the early bactericidal activity (EBA) of sitafloxacin in patients with primary drug-susceptible tuberculosis. In this early bactericidal activity study, 30 patients with primary smear-positive tuberculosis were randomized to the once-daily oral administration of 200 mg sitafloxacin, 500 mg levofloxacin, or 300 mg isoniazid (INH) for 7 days. Sputum for quantitative culture was collected 2 days before the study of drug administration, followed by 16 hours of overnight sputum collected daily for 7 days of monotherapy. Colony-forming units (CFU) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis were counted from the collected overnight sputum on agar plates to calculate the EBA, defined as log10 CFU/mL sputum/day. The bactericidal activity was measured by measuring the first 2 days (early bactericidal activity 0-2) and the last 5 days (prolonged early bactericidal properties 2-7) of study drug administration. The EBA 0-2 of INH (0.39 ± 0.22 log10CFU/mL/day) was higher than that of levofloxacin (0.26 ± 0.27 log10CFU/mL/day) and sitafloxacin (0.22 ± 0.25 log10CFU/mL/day), with no statistically significant difference (P = 0.08). EBA 0-2 was similar for the three drugs. INH prolonged early bactericidal activity (2-7) (0.17 ± 0.16 log10CFU/mL/day) was higher than levofloxacin (0.14 ± 0.10 log10CFU/mL/day) and lower than sitafloxacin (0.26 ± 0.31 log10CFU/mL/day), with no statistically significant difference (P = 0.59). The EBA 2-7 of sitafloxacin showed higher activity than INH and levofloxacin. Sitafloxacin exhibits comparable early bactericidal activity and higher extended early bactericidal activity relative to levofloxacin. In addition, this novel fluoroquinolone has a good safety profile. The study data highlights the potential of sitafloxacin in the clinical management of drug-susceptible tuberculosis, as well as drug-resistant tuberculosis.IMPORTANCESitafloxacin is a quinolone broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, and its pharmacologic properties and in vitro data demonstrate that sitafloxacin has a potent killing effect against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. However, its efficacy in patients with primary-sensitive tuberculosis is unclear. We investigated the early bactericidal activity of sitafloxacin in primary susceptible tuberculosis. The results showed that sitafloxacin exhibited comparable early bactericidal activity and higher extended early bactericidal activity relative to levofloxacin. In addition, this novel fluoroquinolone has a good safety profile. Our study data highlights the potential of sitafloxacin in the clinical management of drug-susceptible tuberculosis, as well as drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Keywords: antituberculosis action; early bactericidal activity; fluoroquinolones; isoniazid; levofloxacin; sitafloxacin; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2022. Rapid communication: key changes to the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis, p 6. World Health Organization, Geneva.
-
- World Health Organization . 2022. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis: module 4: treatment: drug-susceptible tuberculosis treatment. World Health Organization, Geneva. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

