Brain Resident Ly6Chi Monocytes Are Necessary for Maintaining Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
- PMID: 39656489
- PMCID: PMC12339147
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2024.0835
Brain Resident Ly6Chi Monocytes Are Necessary for Maintaining Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
Abstract
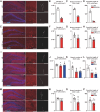
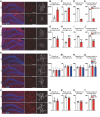
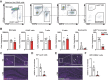
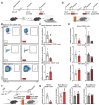
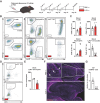
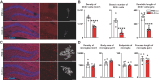
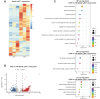
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) is crucial to various brain functions. Neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation and stress can impair AHN, contributing to the development of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Stress is known to extensively affect both the brain and peripheral immune system. However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying stress-induced impairments in AHN remain unclear. In this study, we found that, unlike neuroinflammatory conditions, stress significantly inhibited AHN independently of microglial activation, suggesting a novel mechanism mediating stress-impaired AHN. Since stress modulates peripheral immune cells, we examined the distribution of immune cells infiltrating the brain. We found a significant decrease of infiltrated Ly6Chi monocytes in the brain parenchyma. In the blood, adoptively transferred ZsGreen+ Ly6Chi monocytes drastically reduced due to stress-induced homing to the bone marrow. Adrenalectomy (ADX) experiments revealed that monocyte homing is regulated by glucocorticoid and may cause impairments in AHN. Depleting peripheral circulating monocytes reduced brain-resident Ly6Chi monocytes and replicated the stress-induced inhibition of AHN, independent of microglia activation. RNA sequencing analysis of Ly6Chi monocytes revealed a stress-induced transcriptional profile, suggesting their supportive role in neuronal functions. Together, these findings demonstrate a novel and essential role of brain resident Ly6Chi monocytes in maintaining AHN at basal level, which is important for brain functions.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
