SLAM/SAP signaling regulates discrete γδ T cell developmental checkpoints and shapes the innate-like γδ TCR repertoire
- PMID: 39656519
- PMCID: PMC11630817
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.97229
SLAM/SAP signaling regulates discrete γδ T cell developmental checkpoints and shapes the innate-like γδ TCR repertoire
Abstract
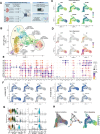
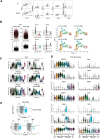
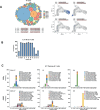
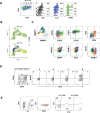
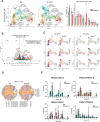
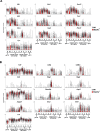
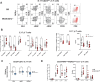
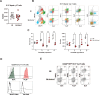
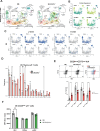
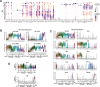
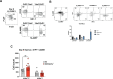
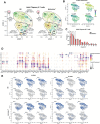
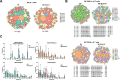
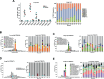
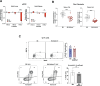
During thymic development, most γδ T cells acquire innate-like characteristics that are critical for their function in tumor surveillance, infectious disease, and tissue repair. The mechanisms, however, that regulate γδ T cell developmental programming remain unclear. Recently, we demonstrated that the SLAM/SAP signaling pathway regulates the development and function of multiple innate-like γδ T cell subsets. Here, we used a single-cell proteogenomics approach to identify SAP-dependent developmental checkpoints and to define the SAP-dependent γδ TCR repertoire in mice. SAP deficiency resulted in both a significant loss of an immature Gzma+Blk+Etv5+Tox2+ γδT17 precursor population and a significant increase in Cd4+Cd8+Rorc+Ptcra+Rag1+ thymic γδ T cells. SAP-dependent diversion of embryonic day 17 thymic γδ T cell clonotypes into the αβ T cell developmental pathway was associated with a decreased frequency of mature clonotypes in neonatal thymus, and an altered γδ TCR repertoire in the periphery. Finally, we identify TRGV4/TRAV13-4(DV7)-expressing T cells as a novel, SAP-dependent Vγ4 γδT1 subset. Together, the data support a model in which SAP-dependent γδ/αβ T cell lineage commitment regulates γδ T cell developmental programming and shapes the γδ TCR repertoire.
Keywords: T cells; gamma delta T cells; immunology; inflammation; mouse; thymic development.
© 2024, Mistri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SM, BH, KH, EA, RS, OD, KH, DG, JR, NS, DM, JB No competing interests declared
Figures


Update of
-
SLAM/SAP signaling regulates discrete γδ T cell developmental checkpoints and shapes the innate-like γδ TCR repertoire.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 2:2024.01.10.575073. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.10.575073. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Dec 10;13:RP97229. doi: 10.7554/eLife.97229. PMID: 38260519 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Benoit P, Sigounas VY, Thompson JL, van Rooijen N, Poynter ME, Wargo MJ, Boyson JE. The role of CD1d-restricted NKT cells in the clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the lung is dependent on the host genetic background. Infection and Immunity. 2015;83:2557–2565. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00015-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

