Detection of periodontal bone loss and periodontitis from 2D dental radiographs via machine learning and deep learning: systematic review employing APPRAISE-AI and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39656957
- PMCID: PMC11979759
- DOI: 10.1093/dmfr/twae070
Detection of periodontal bone loss and periodontitis from 2D dental radiographs via machine learning and deep learning: systematic review employing APPRAISE-AI and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Periodontitis is a serious periodontal infection that damages the soft tissues and bone around teeth and is linked to systemic conditions. Accurate diagnosis and staging, complemented by radiographic evaluation, are vital. This systematic review (PROSPERO ID: CRD42023480552) explores artificial intelligence (AI) applications in assessing alveolar bone loss and periodontitis on dental panoramic and periapical radiographs.
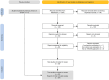
Methods: Five databases (Medline, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane's Library) were searched from January 1990 to January 2024. Keywords related to "artificial intelligence", "Periodontal bone loss/Periodontitis", and "Dental radiographs" were used. Risk of bias and quality assessment of included papers were performed according to the APPRAISE-AI Tool for Quantitative Evaluation of AI Studies for Clinical Decision Support. Meta analysis was carried out via the "metaprop" command in R V3.6.1.
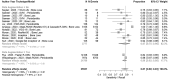
Results: Thirty articles were included in the review, where 10 papers were eligible for meta-analysis. Based on quality scores from the APPRAISE-AI critical appraisal tool of the 30 papers, 1 (3.3%) were of very low quality (score < 40), 3 (10.0%) were of low quality (40 ≤ score < 50), 19 (63.3%) were of intermediate quality (50 ≤ score < 60), and 7 (23.3%) were of high quality (60 ≤ score < 80). No papers were of very high quality (score ≥ 80). Meta-analysis indicated that model performance was generally good, eg, sensitivity 87% (95% CI, 80%-93%), specificity 76% (95% CI, 69%-81%), and accuracy 84% (95% CI, 75%-91%).
Conclusion: Deep learning shows much promise in evaluating periodontal bone levels, although there was some variation in performance. AI studies can lack transparency and reporting standards could be improved. Our systematic review critically assesses the application of deep learning models in detecting alveolar bone loss on dental radiographs using the APPRAISE-AI tool, highlighting their efficacy and identifying areas for improvement, thus advancing the practice of clinical radiology.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; panoramic radiographs; periapical radiographs; periodontitis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology and the International Association of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Vollmer A, Vollmer M, Lang G, et al. Automated assessment of radiographic bone loss in the posterior maxilla utilizing a multi-object detection artificial intelligence algorithm. Appl Sci. 2023;13(3):1858. 10.3390/app13031858 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources