Annual Health Expenditures by Body Mass Index Categories and the Economic Impact of Obesity in Türkiye: A Retrospective Modeling Study
- PMID: 39657615
- PMCID: PMC12101814
- DOI: 10.1159/000542821
Annual Health Expenditures by Body Mass Index Categories and the Economic Impact of Obesity in Türkiye: A Retrospective Modeling Study
Abstract
Introduction: Obesity is considered not only a public health issue on a global scale but also a disease adversely affecting the world economies. Economic impact of overweight and obesity has not yet been investigated in Türkiye at a national level. This study aimed to investigate the impact of obesity on healthcare costs in Türkiye and to estimate the overall national economic burden of obesity.
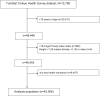
Methods: The study was based on a cross-sectional analysis of retrospectively pooled data from 2009 to 2014 payer claims data and 2014-2019 Türkiye Health Survey (THS). In the first step, obesity-related annual per person overall health expenditures in adults with obesity were calculated and calculations were also made in subgroups of payer and healthcare categories. In the second step, using the developed model, the national economic disease burden of adult obesity was estimated, along with the projections for the estimated expenditures over the next 30 years. Economic values were adjusted according to US dollar values of 2021 purchasing power parities (PPPs) (PPP 1.0 = 2.782 TRY).
Results: The annual healthcare costs were significantly higher in individuals with obesity than in those with normal body mass index (BMI) (odds ratio 1.243; 95% confidence interval: 1.206-1.281), and the cost increment was positively correlated with higher BMI (by 117% in class I obesity vs. 169% in class III obesity, p < 0.001). In the year 2021, obesity-related direct and indirect costs in adults were estimated to be PPP 27.4 billion and 39.5 billion, respectively. The total economic burden was estimated to be PPP 66.9 billion, which is equivalent to 2.6% of gross national product. Direct medical cost of obesity corresponds to 8.4% of total health expenditure in Türkiye.
Conclusions: Obesity is both an individual and social health problem, which emphasizes the potential role of a range of stakeholders, besides the health sector, in addressing this problem. The indirect costs comprise the key cost driver of the total national cost of obesity, which forms the rationale for population-wide policy interventions toward prevention or reduction of obesity.
Keywords: Cost analysis; Health expenditure; Healthcare cost; Obesity.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
L.T. has received honoraria for lectures or consultancy from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Pfizer, and Ultragenyx. V.D.Y. reports honoraria from Eli Lilly for providing a single advisory activity and from Novo Nordisk for providing educational sessions and attending advisory boards. A.S. reports honoraria for advisory board attendance from AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Eczacıbasi, Roche Diagnostics, Daiichi Sankyo, and Sanovel, for principal investigator/director role in clinical trials from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Novartis and fees for serving as a speaker from Bilim Ilac, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, and Medtronic. B.G. and E.S.Y. are employees of Novo Nordisk Turkey. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of body mass index with health care expenditures in the United States by age and sex.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 24;16(3):e0247307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247307. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33760880 Free PMC article.
-
Low-, moderate-, and high-risk obesity in association with cost drivers, costs over the lifecycle, and life expectancy.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 31;24(1):2069. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19574-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39085809 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect costs constitute a major part of the total economic burden of obesity: a Finnish population-based cohort study.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 10;25(1):1739. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22978-9. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40349009 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and overweight in Canada: an updated cost-of-illness study.Obes Rev. 2010 Jan;11(1):31-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00579.x. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Obes Rev. 2010. PMID: 19413707 Review.
-
Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. In 2007.Diabetes Care. 2008 Mar;31(3):596-615. doi: 10.2337/dc08-9017. Diabetes Care. 2008. PMID: 18308683 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity and overweight. Fact sheets. Geneva: WHO; 2021.
-
- WHO [Internet] . European regional obesity report in 2022. [cited 2023 Jan 3]. Available from: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/353747/9789289057738-eng.pdf...
-
- World Obesity Federation [Internet] . World obesity Atlas 2023. [cited 2023 Apr 15]. Available from: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19
-
- Satman I, Yilmaz T, Sengül A, Salman S, Salman F, Uygur S, et al. . Population-based study of diabetes and risk characteristics in Turkey: results of the Turkish diabetes epidemiology study (TURDEP). Diabetes Care. 2002;25(9):1551–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical