Lurbinectedin sensitizes PD-L1 blockade therapy by activating STING-IFN signaling in small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39657664
- PMCID: PMC11722101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101852
Lurbinectedin sensitizes PD-L1 blockade therapy by activating STING-IFN signaling in small-cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Lurbinectedin sensitizes PD-L1 blockade therapy by activating STING-IFN signaling in small-cell lung cancer.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Feb 18;6(2):101944. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101944. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 39827880 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
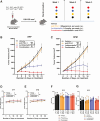
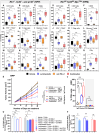
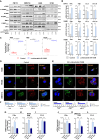
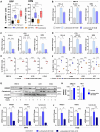
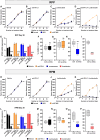
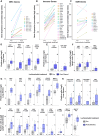
Lurbinectedin is an approved second-line treatment for small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). SCLC clinical trials combining lurbinectedin with PD-L1 blockade are currently ongoing. However, the immunomodulatory effects of lurbinectedin remain largely unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that lurbinectedin treatment activates the STING pathway, which increases interferon (IFN) signaling, pro-inflammatory chemokines, and major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) in SCLC models. Lurbinectedin treatment augments the anti-tumor immune response of PD-L1 blockade with significant tumor regression in first-line and maintenance settings in SCLC mouse models. In vivo, lurbinectedin treatment increases CD8+ T cells and M1 macrophages and decreases immunosuppressive M2 macrophages. STING and CD8 depletion reverses the anti-tumor response. Interestingly, our study shows that lurbinectedin treatment upregulates MHC-I/II genes and CD8 in SCLC clinical samples. We provide mechanistic insights into the effect of lurbinectedin on STING-mediated multimodal immune activation and demonstrate that lurbinectedin treatment represents a promising therapeutic strategy to potentiate the efficacy of immunotherapy in SCLC.
Keywords: MHC-I; PD-L1 blockade; cGAS-STING; immune activation; small-cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.S. has received research grants from Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Debiopharm. T.A.B. received a grant and honorarium from Bristol Meyers Squibb.
Figures

References
-
- Paz-Ares L., Dvorkin M., Chen Y., Reinmuth N., Hotta K., Trukhin D., Statsenko G., Hochmair M.J., Özgüroğlu M., Ji J.H., et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;394:1929–1939. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mahadevan N.R., Knelson E.H., Wolff J.O., Vajdi A., Saigí M., Campisi M., Hong D., Thai T.C., Piel B., Han S., et al. Intrinsic Immunogenicity of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Revealed by Its Cellular Plasticity. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:1952–1969. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0913. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

