Miltefosine reinvigorates exhausted T cells by targeting their bioenergetic state
- PMID: 39657666
- PMCID: PMC11722131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101869
Miltefosine reinvigorates exhausted T cells by targeting their bioenergetic state
Abstract
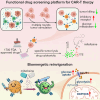
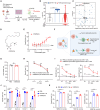
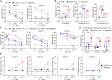
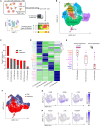
T cell exhaustion presents a major challenge for the efficacy of both immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICBs) and chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell immunotherapies. To address this issue, we generate hypofunctional CAR-T cells that imitate the exhaustion state. By screening a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved small molecule library using this model, we identify miltefosine as a potent molecule that restores the impaired function of CAR-T cells in a PD-1/PD-L1-independent manner. Impressively, in the terminally exhausted state where PD-1 antibody treatment is ineffective, miltefosine still enhances CAR-T cell activity. Single-cell sequencing analysis reveals that miltefosine treatment significantly increases the population of effector cells. Mechanistically, miltefosine improves impaired glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in hypofunctional CAR-T cells. In both allogeneic and syngeneic tumor models, miltefosine effectively enhances the solid tumor clearance ability of CAR-T cells and T cells, demonstrating its potential as an effective immunotherapeutic drug.
Keywords: T cell exhaustion; glycolytic metabolism; high-throughput drug screening; immunotherapy for solid tumors; miltefosine.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wherry E.J. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2011;12:492–499. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

