Novel BRCA1-PLK1-CIP2A axis orchestrates homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair to maintain chromosome integrity during oocyte meiosis
- PMID: 39657788
- PMCID: PMC11754672
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1207
Novel BRCA1-PLK1-CIP2A axis orchestrates homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair to maintain chromosome integrity during oocyte meiosis
Abstract
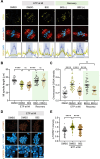
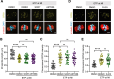
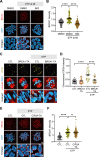
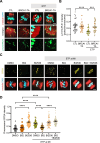
Double-strand breaks (DSBs) are a formidable threat to genome integrity, potentially leading to cancer and various genetic diseases. The prolonged lifespan of mammalian oocytes increases their susceptibility to DNA damage over time. While somatic cells suppress DSB repair during mitosis, oocytes exhibit a remarkable capacity to repair DSBs during meiotic maturation. However, the precise mechanisms underlying DSB repair in oocytes remain poorly understood. Here, we describe the pivotal role of the BRCA1-PLK1-CIP2A axis in safeguarding genomic integrity during meiotic maturation in oocytes. We found that inhibition of homologous recombination (HR) severely impaired chromosome integrity by generating chromosome fragments during meiotic maturation. Notably, HR inhibition impaired the recruitment of CIP2A to damaged chromosomes, and the depletion of CIP2A led to chromosome fragmentation following DSB induction. Moreover, BRCA1 depletion impaired chromosomal recruitment of CIP2A, but not vice versa. Importantly, the impaired chromosomal recruitment of CIP2A could be rescued by PLK1 inhibition. Consequently, our findings not only underscore the importance of the chromosomal recruitment of CIP2A in preventing chromosome fragmentation, but also demonstrate the regulatory role of the BRCA1-PLK1-CIP2A axis in this process during oocyte meiotic maturation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1 mediates BRCA1 phosphorylation and recruitment at DNA double-strand breaks.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 19;7(3):2269-83. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6825. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26745677 Free PMC article.
-
CIP2A acts as a scaffold for CEP192-mediated microtubule organizing center assembly by recruiting Plk1 and aurora A during meiotic maturation.Development. 2017 Oct 15;144(20):3829-3839. doi: 10.1242/dev.158584. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Development. 2017. PMID: 28935709
-
Oocytes can repair DNA damage during meiosis via a microtubule-dependent recruitment of CIP2A-MDC1-TOPBP1 complex from spindle pole to chromosomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 9;51(10):4899-4913. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad213. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36999590 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-Like Kinase 1 and DNA Damage Response.DNA Cell Biol. 2024 Sep;43(9):430-437. doi: 10.1089/dna.2024.0018. Epub 2024 Jul 3. DNA Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38959179 Review.
-
BRCA-related ATM-mediated DNA double-strand break repair and ovarian aging.Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Jan 1;26(1):43-57. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz043. Hum Reprod Update. 2020. PMID: 31822904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-targeting reverse genetic approaches: the future of oocyte and preimplantation embryo research.Mol Hum Reprod. 2025 Apr 3;31(2):gaaf008. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaaf008. Mol Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40100642 Review.
References
-
- Shrivastav M., De Haro L., Nickoloff J.A.. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell Res. 2008; 18:134–147. - PubMed
-
- Rogakou E.P., Pilch D.R., Orr A.H., Ivanova V.S., Bonner W.M.. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998; 273:5858–5868. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

