PDGFRA is a conserved HAND2 effector during early cardiac development
- PMID: 39658721
- PMCID: PMC11634778
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-024-00574-1
PDGFRA is a conserved HAND2 effector during early cardiac development
Abstract
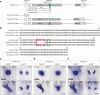
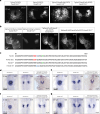
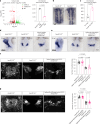
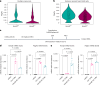
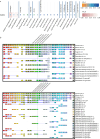
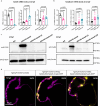
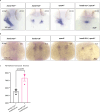
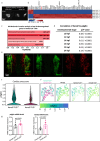
The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor HAND2 has multiple roles during vertebrate organogenesis, including cardiogenesis. However, much remains to be uncovered about its mechanism of action. Here, we show the generation of several hand2 mutant alleles in zebrafish and demonstrate that dimerization-deficient mutants display the null phenotype but DNA-binding-deficient mutants do not. Rescue experiments with Hand2 variants using a newly identified hand2 enhancer confirmed these observations. To identify Hand2 effectors critical for cardiogenesis, we analyzed the transcriptomes of hand2 loss- and gain-of-function embryonic cardiomyocytes and tested the function of eight candidate genes in vivo; pdgfra was most effective in rescuing myocardial migration in hand2 mutants. Accordingly, we identified a putative Hand2-binding region in the zebrafish pdgfra locus that is important for its expression. In addition, Hand2 loss- and gain-of-function experiments in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac cells decreased and increased Pdgfra expression, respectively. Altogether, these results further our mechanistic understanding of HAND2 function during early cardiogenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





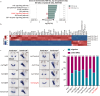
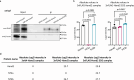
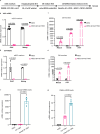
References
-
- Stainier, D. Y., Lee, R. K. & Fishman, M. C. Cardiovascular development in the zebrafish. I. Myocardial fate map and heart tube formation. Development119, 31–40 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Garg, V. et al. GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature424, 443–447 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Jiang, J.-Q. et al. Prevalence and spectrum of GATA5 mutations associated with congenital heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol.165, 570–573 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
