Prevalence and clinical significance of Claudin-3 expression in cancer: a tissue microarray study on 14,966 tumor samples
- PMID: 39658782
- PMCID: PMC11633013
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00702-w
Prevalence and clinical significance of Claudin-3 expression in cancer: a tissue microarray study on 14,966 tumor samples
Abstract
Background: Claudin-3 (CLDN3) participates in the formation of the tight-junctions (TJs) that regulate intercellular permeability. Altered CLDN3 expression has been linked to tumor progression in multiple tumor types. Despite its widespread expression in normal epithelial cells, CLDN3 is considered an attractive drug target candidate, since it may be more accessible in cancer cells than in normal cells due to their less orchestrated cell growth.
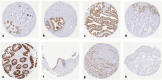
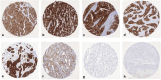
Methods: To comprehensively determine the prevalence of CLDN3 expression in cancer, a tissue microarray containing 14,966 samples from 133 different tumor types and subtypes as well as 608 samples of 76 different normal tissue types was analyzed by immunohistochemistry.
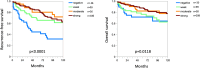
Results: CLDN3 immunostaining was observed in 8,479 (68.9%) of 12,314 analyzable tumors, including 11.6% with weak, 6.2% with moderate, and 51.1% with strong positivity. CLDN3 staining was found in 96 of 133 tumor categories, 80 of which contained at least one strongly positive case. CLDN3 positivity was most seen in neuroendocrine neoplasms (92-100%) and in adenocarcinomas (67-100%), tumors of the female genital tract, including various subtypes of ovarian and endometrial carcinoma (up to 100%), as well as different subtypes of breast cancer (95.3-100%). CLDN3 positivity was less common in squamous cell carcinomas (0-43.2%) and mainly absent in melanoma, mesenchymal, and hematolymphatic neoplasms. In clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), low CLDN3 was strongly linked to poor ISUP (p < 0.0001), Fuhrman (p < 0.0001), and Thoenes (p < 0.0001) grades, advanced pT category (p < 0.0001), high UICC stage (p = 0.0006) and distant metastasis (p = 0.0011), as well as shortened overall (p = 0.0118) and recurrence-free (p < 0.0001) survival. In papillary RCC (pRCC), low CLDN3 was associated with poor grade (p < 0.05), high pT (p = 0.0273) and distant metastasis (p = 0.0357). In urothelial carcinoma high CLDN3 was linked to high grade (p < 0.0001) and nodal metastasis (p = 0.0111). The level of CLDN3 staining was unrelated to parameters of tumor aggressiveness in pancreatic, gastric, and breast cancer.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our data demonstrate significant levels of CLDN3 expression in many different tumor entities and identify reduced CLDN3 expression as a potential prognostic marker in RCC.
Keywords: Biomarker; CLDN3; Cancer; Renal cell carcinoma; Tissue microarray.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The use of archived remnants of diagnostic tissues for manufacturing of TMAs and their analysis for research purposes as well as patient data analysis has been approved by local laws (HmbKHG, §12) and by the local ethics committee (Ethics commission Hamburg, WF-049/09). All work has been carried out in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Patient consent was waived due to local laws (HmbKHG, §12,1) that permit research with anonymized diagnostic left-over tissue samples. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Conflict of interests The CLDN3 antibody clone HMV-309 was provided from ardoci GmbH (owned by a family member of GS).
Figures

References
-
- Tsukita S, Tanaka H, Tamura A. The Claudins: from tight junctions to biological systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019;44:141–52. - PubMed
-
- Milatz S, et al. Claudin-3 acts as a sealing component of the tight junction for ions of either charge and uncharged solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1798:2048–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

