Association between the systemic immune-inflammation index and the outcome of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 39659620
- PMCID: PMC11628305
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1486503
Association between the systemic immune-inflammation index and the outcome of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: Risk factors that influence the outcome of patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) are not fully understood. The systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) is an independent prognostic factor for multiple diseases. However, the impact of the SII on the outcome of liver fibrosis is unclear.
Methods: This prospective real-world study enrolled patients with CHC treated with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir. Logistic regression models were used to investigate the relationship between the SII and the outcome of liver fibrosis in treatment-naive patients. Liver fibrosis was assessed using aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) and fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4).
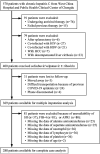
Results: Of the 288 participants, the SII was 238.2 (153.0-358.2). The non-improved outcomes of liver fibrosis assessed with APRI (non-improved APRI) and FIB-4 (non-improved FIB-4) were 83.0 and 87.5%, respectively. Adjusted models showed that the SII was positively associated with non-improved APRI (adjusted OR (95% CI): 1.013 (1.009-1.017), p < 0.001) and FIB-4 (adjusted OR (95% CI): 1.004 (1.001-1.007), p = 0.012). Similarly, a higher SII was associated with a higher risk of non-improved APRI (adjusted OR (95% CI): 13.53 (5.60-32.68), p < 0.001) and FIB-4 (adjusted OR (95% CI): 5.69 (2.17-14.90), p < 0.001). The association with non-improved APRI was much more remarkable in patients with alanine aminotransferase <2 ULN, and the association with non-improved FIB-4 was remarkable in patients aged <50 years. Multiple imputation analyses confirmed the robustness of these results.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that the SII was positively associated with non-improved outcomes of liver fibrosis in patients with CHC. These results need to be validated in large-scale prospective cohorts.
Keywords: chronic hepatitis C; liver fibrosis; outcome; risk factor; systemic immune-inflammation index.
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Wang, Du and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

