Tranexamic Acid Application in Facial Aesthetic Surgery: An Umbrella Review
- PMID: 39659743
- PMCID: PMC11630850
- DOI: 10.1093/asjof/ojae105
Tranexamic Acid Application in Facial Aesthetic Surgery: An Umbrella Review
Abstract
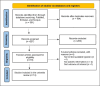
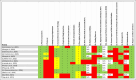
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is an antifibrinolytic agent that is considered as one of the latest interventions currently being investigated in the field of facial aesthetic surgeries, as it is predicted to be effective in reducing intraoperative and postoperative complications of facial aesthetic surgeries. This review focuses on giving readers a comprehensive overview regarding the use of TXA in facial aesthetic surgeries. In this umbrella review, data were extracted from existing systematic reviews and meta-analysis that focused on the use of TXA in facial aesthetic surgeries. The authors searched PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases. The data were extracted using a standard format, and the AMSTAR-2 (A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews) tool was used to assess the quality of the included reviews. In total, this study included 14 systematic reviews and meta-analyses all of which evaluated the effect of TXA on facial aesthetic surgeries, which included rhinoplasty, septorhinoplasty, rhytidectomy, and blepharoplasty. The majority of the included studies focused on reporting the effect of TXA on blood loss volume (BLV) and duration of surgery (DOS) as well as other postoperative complications. Eleven out of the 12 studies that focused on rhinoplasty showed that TXA used reduced BLV. In addition, in 8 studies that were focusing on DOS, the majority showed a reduction in DOS with TXA use. While in the case of septorhinoplasty, 3 studies revealed that TXA use decreased BLV. Moreover, in the case of rhytidectomy, 3 out of 6 systematic reviews showed reduction in BLV, while 2 reported reductions in DOS. Finally, the authors conclude that the use of TXA is indeed efficient in reducing BLV and DOS, in addition to some of the complications that can occur during or after facial aesthetic surgeries. However, in order to reach a final decision on the implication of the use of TXA in facial aesthetic surgeries, further studies should be established using a standardized protocol in assessing the desired outcomes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Aesthetic Society.
Figures
References
-
- Jimenez JJ, Iribarren JL, Lorente L, et al. . Tranexamic acid attenuates inflammatory response in cardiopulmonary bypass surgery through blockade of fibrinolysis: a case control study followed by a randomized double-blind controlled trial. Crit Care. 2007;11:R117. doi: 10.1186/cc6173 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources