Exogenous expression of ATP8, a mitochondrial encoded protein, from the nucleus in vivo
- PMID: 39659757
- PMCID: PMC11629202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101372
Exogenous expression of ATP8, a mitochondrial encoded protein, from the nucleus in vivo
Abstract
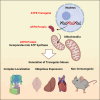
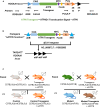
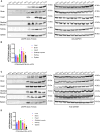
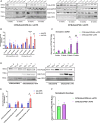
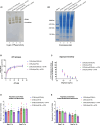
Replicative errors, inefficient repair, and proximity to sites of reactive oxygen species production make mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) susceptible to damage with time. We explore in vivo allotopic expression (re-engineering mitochondrial genes and expressing them from the nucleus) as an approach to rescue defects arising from mtDNA mutations. We used a mouse strain C57BL/6J(mtFVB) with a natural polymorphism (m.7778 G>T) in the mitochondrial ATP8 gene that encodes a protein subunit of the ATP synthase. We generated a transgenic mouse with an epitope-tagged recoded mitochondrial-targeted ATP8 gene expressed from the ROSA26 locus in the nucleus and used the C57BL/6J(mtFVB) strain to verify successful incorporation. The allotopically expressed ATP8 protein in transgenic mice was constitutively expressed across all tested tissues, successfully transported into the mitochondria, and incorporated into ATP synthase. The ATP synthase with transgene had similar activity to non-transgenic control, suggesting successful integration and function. Exogenous ATP8 protein had no negative impact on measured mitochondrial function, metabolism, or behavior. Successful allotopic expression of a mitochondrially encoded protein in vivo in a mammal is a step toward utilizing allotopic expression as a gene therapy in humans to repair physiological consequences of mtDNA defects that may accumulate in congenital mitochondrial diseases or with age.
Keywords: ATP8 gene; allotopic expression; in vivo gene therapy; mitochondrial DNA mutation; mtDNA; safe harbor expression; transgenic mouse.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent application has been filed on the "Allotopic expression of mtDNA genes" in 2023 in the USA (PCT/US23/76302) (B.D. and A.B.). The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Gerbitz K.D., Obermaier-Kusser B., Lestienne P., Zierz S., Müller-Höcker J., Pongratz D., Paetzke-Brunner I., Deufel T. Mutations of the mitochondrial DNA: the contribution of DNA techniques to the diagnosis of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1990;28:241–250. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1990.28.4.241. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

