The diagnostic efficacy of seven autoantibodies in early detection of ground-glass nodular lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39659784
- PMCID: PMC11628369
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1499140
The diagnostic efficacy of seven autoantibodies in early detection of ground-glass nodular lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Persistent ground-glass nodules (GGNs) carry a potential risk of malignancy, however, early diagnosis remained challenging. This study aimed to investigate the cut-off values of seven autoantibodies in patients with ground-glass nodules smaller than 3cm, and to construct machine learning models to assess the diagnostic value of these autoantibodies.
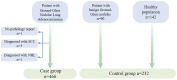
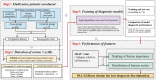
Methods: In this multi-center retrospective study, we collected peripheral blood specimens from a total of 698 patients. A total of 466 patients with ground-glass nodular lung adenocarcinoma no more than 3cm were identified as a case group based on pathological reports and imaging data, and control group (n=232) of patients consisted of 90 patients with benign nodules and 142 patients with health check-ups. Seven antibodies were quantified in the serum of all participants using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the working characteristic curves of the subjects were plotted to determine the cut-off values of the seven autoantibodies related ground-glass nodular lung adenocarcinoma early. Subsequently, the patients were randomly divided into a training and test set at a 7:3 ratio. Eight machine-learning models were constructed to compare the diagnostic performances of multiple models. The model performances were evaluated using sensitivity, specificity, and the area under the curve (AUC).
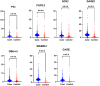
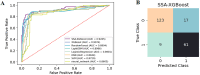
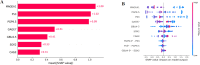
Results: The serum levels of the seven autoantibodies in case group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The combination of the seven autoantibodies demonstrated a significantly enhanced diagnostic efficacy in identifying ground-glass nodular lung adenocarcinoma early when compared to the diagnostic efficacy of the autoantibodies when used respectively. The combined diagnostic approach of the seven autoantibodies exhibited a sensitivity of 84.05%, specificity of 91.85%, and AUC of 0.8870, surpassing the performance of each autoantibody used individually. Furthermore, we determined that Sparrow Search Algorithm-XGBoost (SSA-XGBOOST) had the best diagnostic performance among the models (AUC=0.9265), with MAGEA1, P53, and PGP9.5 having significant feature weight proportions.
Conclusions: Our research assessed the diagnostic performance of seven autoantibodies in patients with ground-glass nodules for benign-malignant distinction, and the nodules are all no more than 3cm especially. Our study set cut-off values for seven autoantibodies in identifying GGNs no more than 3cm and constructed a machine learning model for effective diagnosis. This provides a non-invasive and highly discriminative method for the evaluation of ground-glass nodules in high-risk patients.
Keywords: autoantibodies; diagnosis; early detection; ground-glass nodules; lung adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Zhao, Li, Wu, Yu, Wang, Wei, Wang, Liu, Yin, Yang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

