Retrospective Comparison of Early Versus Late Initiation of Long-Acting Insulin in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients in Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- PMID: 39659852
- PMCID: PMC11627569
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-29.6.614
Retrospective Comparison of Early Versus Late Initiation of Long-Acting Insulin in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients in Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Abstract
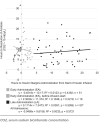
Objective: Determine whether early administration (EA) of long-acting insulin in pediatric diabetic -ketoacidosis (DKA) reduces time to acidosis resolution while maintaining safety when compared with late administration (LA).
Methods: This retrospective review compared EA (within 4 hours) to LA (4 to 24 hours) of long-acting insulin in DKA management in the pediatric intensive care unit between 2015 and 2022. Admissions were excluded for patients ≥18 years of age, without type 1 diabetes, with insufficient laboratory data, or who did not receive insulin glargine within 24 hours of starting treatment. Primary outcome was resolution of acidosis, measured as time to normalization of serum sodium bicarbonate concentration (>15 mEq/L). Secondary outcomes included hospital and intensive care lengths of stay, and insulin infusion duration. Safety outcomes were hypokalemia, hypoglycemia, and cerebral edema.
Results: Of the 233 admissions evaluated, 51 met inclusion for each group. The median patient age was 11 years, 42% female, and 59% had new-onset diabetes. No difference was found in the median time to acidosis resolution (8.13 hours [EA] and 8.02 hours [LA]; p = 0.4161). Median insulin infusion durations were 16.2 and 17.6 hours for EA and LA, respectively (p = 0.8750). Median hospital stay was 2 days for both groups (p = 0.9068). Hypoglycemia and hypokalemia rates were not significantly different but occurred more often than previously reported.
Conclusions: Early administration of long-acting insulin in pediatric DKA did not affect acidosis duration or treatment length when compared with late administration. Incidence of hypoglycemia and hypokalemia were similar between groups.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus type 1; diabetic ketoacidosis; hypoglycemia; hypokalemia; insulin; insulin glargine; intensive care units; long-acting; pediatric.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: membership@pediatricpharmacy.org.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure. The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts, and honoraria. The authors had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Smith CP, Firth D, Bennett S, et al. Ketoacidosis occurring in newly diagnosed and established diabetic children. Acta Paediatr . 1998;87(5):537–541. - PubMed
-
- Ramphul K, Joynauth J. An update on the incidence and burden of diabetic ketoacidosis in the US [published correction appears in Diabetes Care. 2022;45(7):1698] Diabetes Care . 2020;43(12):e196–e197. - PubMed
-
- Wolfsdorf JI, Glaser N, Agus M, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes . 2018;19((suppl 27)):155–177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous