Association Between Sleep Quality and Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy: A Prospective Case-Control Study
- PMID: 39659893
- PMCID: PMC11630714
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S482592
Association Between Sleep Quality and Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy: A Prospective Case-Control Study
Abstract
Objective: The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the changes in sleep quality among patients with cirrhotic cardiomyopathy (CCM).
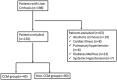
Methods: The study included liver cirrhosis patients aged 18-75 from Northern Jiangsu People's Hospital Affiliated to Yangzhou University and collected their clinical examination results to assess the clinical characteristics and related risk factors of patients with CCM.
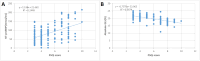
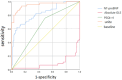
Results: The study found that the onset of CCM was not related to the etiology of inducing cirrhosis. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) score (odds ratio (OR) = 13.476, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.514-119.923, P = 0.020), absolute GLS (OR = 0.328, 95% CI = 0.210-0.510, P < 0.001), and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (OR = 1.050, 95% CI = 1.025-1.076, P < 0.001) were identified as independent risk factors for inducing CCM.
Conclusion: In patients with CCM, a decrease in sleep quality often occurs. When cirrhotic patients also have poor sleep quality, along with a decrease in absolute Global Left Ventricular Strain (GLS) levels and an increase in NT-proBNP levels, these factors may pose a higher risk for CCM development. However, further validation of these research findings is required in larger sample sizes.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; cirrhotic cardiomyopathy; liver cirrhosis; sleep quality.
© 2024 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

