Risk factors of positive lymph node metastasis after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer and construction of prediction models
- PMID: 39659931
- PMCID: PMC11626280
- DOI: 10.62347/PEDV7297
Risk factors of positive lymph node metastasis after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer and construction of prediction models
Abstract
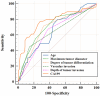
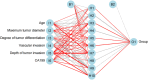
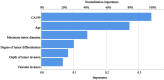
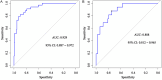
Positive lymph node metastasis after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer is a key factor affecting the prognosis of patients, and its mechanism is complex and multifactorial. The aim of this study is to identify the relevant risk factors for positive lymph node metastasis after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer, and to construct corresponding predictive models. Through a retrospective analysis of clinical data of 316 gastric cancer patients who underwent radical surgery for gastric cancer, we found that age, maximum tumor diameter, degree of tumor differentiation, vascular invasion, depth of tumor infiltration, and CA199 were important factors affecting lymph node metastasis positivity in gastric cancer patients. Based on these factors, we constructed a Nomogram prediction model and found through internal validation that the model has good predictive performance. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of the training and validation sets were 0.929 and 0.888, respectively. Clinical data of another 390 patients were collected for external verification. External validation results showed that the model had a predictive sensitivity of 75.76% (50/66), a specificity of 91.05% (295/324), and an accuracy of 88.46% (345/390). In addition, we also constructed a neural network prediction model and compared it with the Nomogram model. The results showed that the prediction performance of the Nomogram model was similar to that of the neural network model. The Nomogram model has been validated internally and externally, demonstrating high discrimination and accuracy, providing a convenient, intuitive, and personalized evaluation tool for clinicians, helping to optimize the postoperative management of gastric cancer patients and improve prognosis.
Keywords: Radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer; logistic regression analysis; lymph node metastasis; neural network model; nomogram model.
AJCR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Wang FH, Zhang XT, Tang L, Wu Q, Cai MY, Li YF, Qu XJ, Qiu H, Zhang YJ, Ying JE, Zhang J, Sun LY, Lin RB, Wang C, Liu H, Qiu MZ, Guan WL, Rao SX, Ji JF, Xin Y, Sheng WQ, Xu HM, Zhou ZW, Zhou AP, Jin J, Yuan XL, Bi F, Liu TS, Liang H, Zhang YQ, Li GX, Liang J, Liu BR, Shen L, Li J, Xu RH. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer, 2023. Cancer Commun (Lond) 2024;44:127–172. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu P, Huang X, Huang L, Dai G, Xu Q, Fang J, Ye Z, Chai T, Du Y. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) plus systemic chemotherapy versus systemic chemotherapy alone in locally advanced gastric cancer after D2 radical resection: a randomized-controlled study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149:11491–11498. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
