Charting the therapeutic landscape: a comprehensive evidence map on medical cannabis for health outcomes
- PMID: 39660005
- PMCID: PMC11628280
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1494492
Charting the therapeutic landscape: a comprehensive evidence map on medical cannabis for health outcomes
Abstract
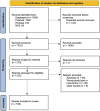
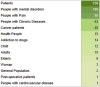
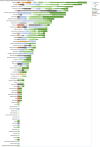
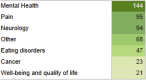
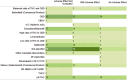
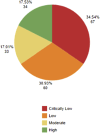
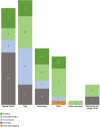
The therapeutic potential of medical cannabis has garnered significant attention in recent years, prompting an urgent need for a comprehensive understanding of its effectiveness across various health outcomes. This article presents an Evidence Map that systematically summarizes clinical evidence on the use of medical cannabis, including the health conditions it addresses, the interventions employed, and the resulting clinical outcomes. The objective is to map the effectiveness of medical cannabis in relation to a wide range of health outcomes. The systematic review process involved two independent, blinded literature researchers who screened the search output using Rayyan software. For studies deemed relevant, full texts were obtained to clarify inclusion or exclusion criteria, and any disagreements were resolved through group discussion. Out of 1,840 initial references, 279 potential studies were selected and read in full, resulting in the inclusion of 194 studies in this evidence map. The results highlight the use of various cannabis formulations, including those based on isolated cannabidiol (CBD). Seventy-one distinct health outcomes were identified in the systematic reviews, with the most reported outcomes being related to various types of pain and patient safety. Other frequently studied outcomes included appetite regulation, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, and muscle spasticity. Notably, 278 out of 489 descriptions of treatment effects for these health outcomes reported either "Positive" or "Potentially Positive" effects. When considering only high-quality systematic reviews, as evaluated by the AMSTAR 2 tool, 42 out of 67 descriptions of treatment effects for up to 20 health outcomes were classified as "Positive" or "Potentially Positive." These outcomes included pain, insomnia, seizures, anxiety, muscle spasticity, multiple sclerosis, urinary incontinence, anorexia, and patient safety. This evidence map provides a comprehensive overview of the current clinical evidence on medical cannabis, highlighting its potential therapeutic benefits across a range of health conditions and emphasizing the need for further high-quality research.
Keywords: CBD; cannabis products; complementary therapies; evidence map; integrative medicine; medical cannabis; public health.
Copyright © 2024 Montagner, de Salas Quiroga, Ferreira, Duarte da Luz, Ruppelt, Schlechta Portella, Abdala, Tabach, Ghelman, Blesching, Perfeito and Schveitzer.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JP was employed by GMESP. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bero L., Li T., Rittiphairoj T., Piper C., Wang S., Brooks-Russell A., et al. (2021). Available at: https://viz-public.cu.edu/t/Anschutz/views/EvidenceMap/Home?%3Aembed=y&%....
-
- Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (2024). Relatório de análise de impacto regulatório sobre produtos de cannabis para fins medicinais. Available at: https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br/assuntos/regulamentacao/air/analises-de-... (Accessed July 18, 2024).
-
- European Medicines Agency (2024). Epidyolex (cannabidiol). Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/epidyolex (Accessed July 19, 2024).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

