Vascular and inflammatory biomarkers of cardiovascular events in non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug users
- PMID: 39660078
- PMCID: PMC11630077
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeae088
Vascular and inflammatory biomarkers of cardiovascular events in non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug users
Abstract
Aims: The Standard care vs. Celecoxib Outcome Trial (SCOT) found similar risk of cardiovascular events with traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and the cyclooxygenase-2-selective drug celecoxib. While pre-clinical work has suggested roles for vascular and renal dysfunction in NSAID cardiovascular toxicity, our understanding of these mechanisms remains incomplete. A post hoc analysis of the SCOT cohort was performed to identify clinical risk factors and circulating biomarkers of cardiovascular events in NSAID users.
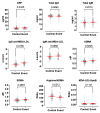
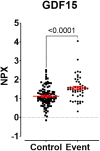
Methods and results: Within SCOT (7295 NSAID users with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis), clinical risk factors associated with cardiovascular events were identified using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression. A nested case-control study of serum biomarkers including targeted proteomics was performed in individuals who experienced a cardiovascular event within 1 year (n = 49), matched 2:1 with controls who did not (n = 97). Risk factors significantly associated with cardiovascular events included increasing age, male sex, smoking, total cholesterol:HDL ratio ≥5, and aspirin use. Statin use was cardioprotective [odds ratio (OR) 0.68; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.46-0.98]. There was significantly higher immunoglobulin (Ig)G anti-malondialdehyde-modified LDL (MDA-LDL), asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), and lower arginine/ADMA. Targeted proteomic analysis identified serum growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) as a candidate biomarker [area under the curve of 0.715 (95% CI 0.63-0.81)].
Conclusion: Growth differentiation factor 15 has been identified as a candidate biomarker and should be explored for its mechanistic contribution to NSAID cardiovascular toxicity, particularly given the remarkable providence that GDF-15 was originally described as NSAID-activated gene-1.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cardiovascular; NSAID; Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Pfizer funded the SCOT study from which the samples for this study were obtained. They had no role in this study. T.M.M. has received consulting fees from Novartis and AstraZeneca and was the Chief investigator for the SCOT study. I.S.M. has received consultancy fees from Astrazeneca and payment from Novartis and NovoNordisk and was a co-investigator for the SCOT study. J.A.M. is a member of the scientific advisory board of Antibe Therapeutics, which develops cyclooxygenase inhibitor anti-inflammatory drugs. J.A.M. and N.S.K. hold active research grant funding in the area of cyclooxygenase biology. R.V. previously held grant funding in this area.
Figures



References
-
- Mitchell JA, Kirkby NS, Ahmetaj-Shala B, Armstrong PC, Crescente M, Ferreira P, Lopes Pires ME, Vaja R, Warner TD. Cyclooxygenases and the cardiovascular system. Pharmacol Ther 2021;217:107624. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald TM, Hawkey CJ, Ford I, McMurray JJ, Scheiman JM, Hallas J, Findlay E, Grobbee DE, Hobbs FR, Ralston SH, Reid DM. Randomized trial of switching from prescribed non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prescribed celecoxib: the Standard care vs. Celecoxib Outcome Trial (SCOT). Eur Heart J 2017;38:1843–1850. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nissen SE, Yeomans ND, Solomon DH, Lüscher TF, Libby P, Husni ME, Graham DY, Borer JS, Wisniewski LM, Wolski KE, Wang Q, Menon V, Ruschitzka F, Gaffney M, Beckerman B, Berger MF, Bao W, Lincoff AM. Cardiovascular safety of celecoxib, naproxen, or ibuprofen for arthritis. N Engl J Med 2016;375:2519–2529. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald TM, Mackenzie IS, Wei L, Hawkey CJ, Ford I. Methodology of a large prospective, randomised, open, blinded endpoint streamlined safety study of celecoxib versus traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis: protocol of the Standard care versus Celecoxib Outcome Trial (SCOT). BMJ Open 2013;3:e002295. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

